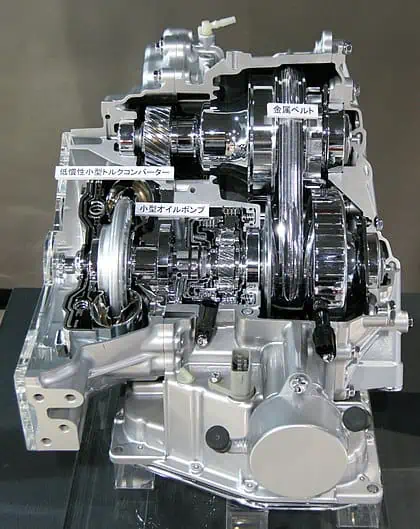
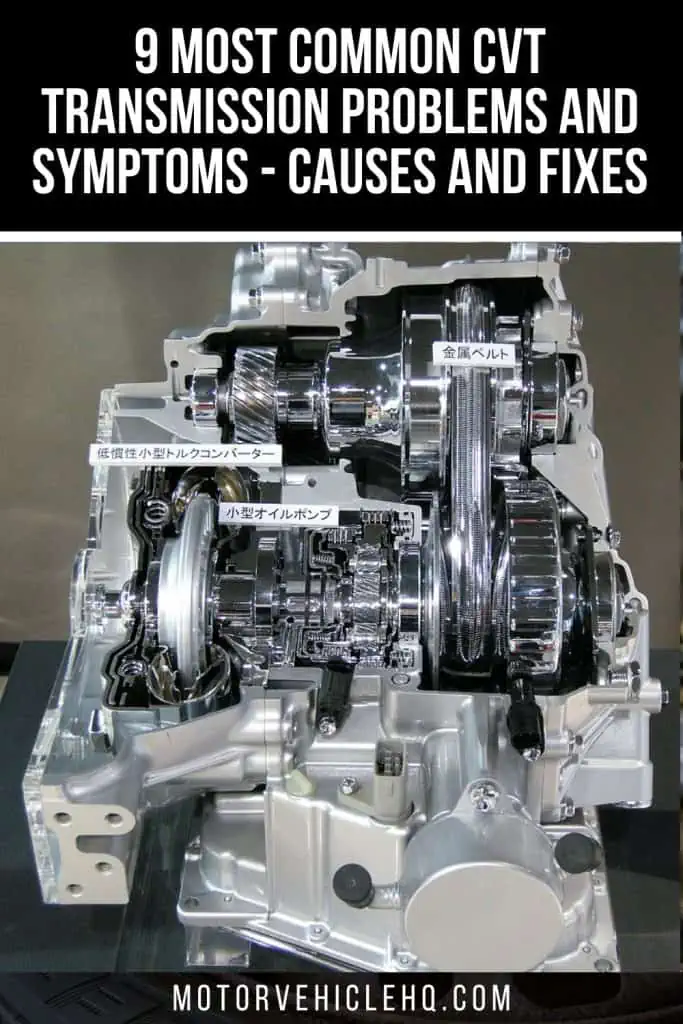
There were just manual and automatic transmissions available decades ago. The CVT is quickly rising to prominence among the transmissions used in contemporary vehicles, thanks to advancements in the automotive industry.
Nonetheless, you would need to be aware of the more typical CVT transmission problems before purchasing such a vehicle. So now you are aware of what to anticipate when purchasing a vehicle with a CVT transmission.
This page will cover a wide range of topics related to CVT transmission, including its history, different varieties, how it operates, which cars typically have one, and some of the most frequent issues.
Issues with CVT Transmissions: CVT transmissions have a poor reputation. Anyone who has experienced a CVT nightmare can comprehend why, but millions of people travel with them every day.
CVT gearboxes have never had a problem. In addition to new automobiles, there are also high-mileage cars. We were already perplexed by CVT transmissions when we conducted the study for this post.
For instance, you came across discussion posts and lawsuits of people who encountered complete CVT breakdowns before their cars reached 50,000 kilometers. These people claimed, primarily on forums, that their CVT gearboxes easily lasted 300,000 kilometers (200,000 miles) (30,000 miles).
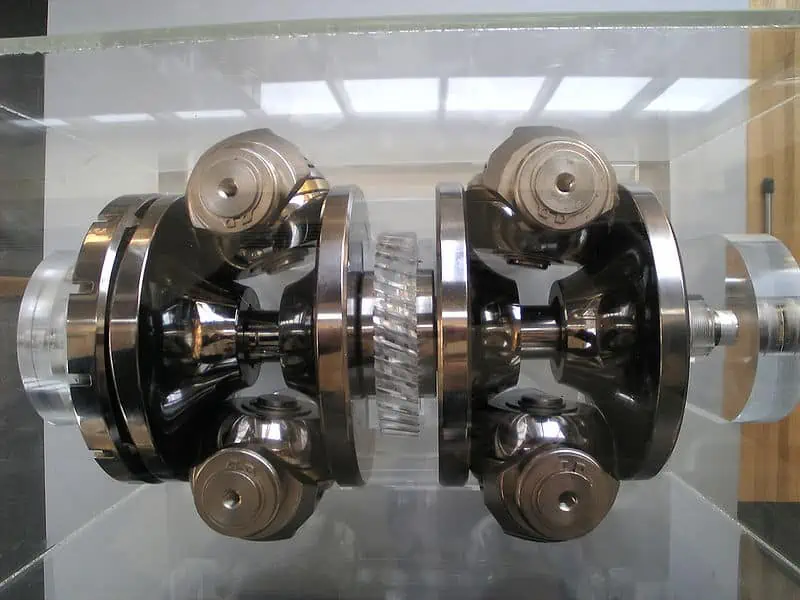
A continuously variable transmission by Hatsukari715. Around 1910, Zenith motorcycles featured CVT transmissions, but Subaru didn’t make the technology widely available until the late 1980s. Especially when it comes to their portfolio of compact and mid-sized automobiles, car manufacturers now virtually never provide a model without a CVT system. A CVT system is essentially an automatic gearbox because it doesn’t need a clutch pedal as a manual transmission does.
This encouraged us to conduct additional research, which we shall discuss in this post. Read our guide, which we issued last week, to learn more about CVT transmissions.
We’ll go over the most typical CVT transmission problems And Symptoms, what particular automakers do with CVTs, and our suggestions.
How Is a CVT Transmission Defined?
Continuously Variable Transmission is known as CVT. Although the design has been around for millennia, it has only lately become popular due to advancements in efficiency. It was created by Leonardo DaVinci in 1490, but Daimler and Benz received the official patent in 1886.
Zenith motorbikes had CVT gearboxes by 1910, while Subaru introduced the technology to the general public in the late 1980s. Nowadays, a car manufacturer hardly ever offers a model without a CVT system, especially when it comes to their lineup of compact and mid-sized cars.
Instead of requiring a clutch pedal like a manual transmission, a CVT system is effectively an automatic transmission. This enables the car to smoothly switch between several effective gear ratio ranges while it is moving.
It stands out from other types of mechanical transmissions because they have harsh changes between gear ratios and offer a limited range of gear ratios.
The CVT system’s shiftless nature offers unmatched flexibility and consistent angular velocity regardless of output speed.
As a result, the car accelerates more smoothly, its fuel efficiency increases, and the whole driving experience is enhanced. How does the CVT system function then?
Without gears, the CVT transmission system can operate. Instead, it is constructed using twin pulleys that are attached to the car’s engine and wheels. A flexible chain or belt connects the two pulleys, enabling them to operate together.
The secret to how the CVT works is that the width of the pulleys varies according to how much power the car requires.
That implies that while one pulley grows, the other one shrinks. Unlike conventional transmission systems, the two pulleys are flexible enough to enable an infinite number of gear ratios.
Even though gears are not necessary, some CVT systems are built to function similarly to gear-based transmission systems. Such CVT gearboxes operate based on movement to predetermined points made possible by conventional shift levers or paddle shifters.
Curiously, not all CVT systems are created equal. Below are the several CVT systems seen in contemporary cars:
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) drive belt by Benutzer:Thomas Ihle / CC BY-SA 3.0. The trouble with CVT transmission issues is that many of them are hard to identify. Many signs can point to a variety of problems because CVT systems have an infinite number of gear ratios and operate with two pulleys hence there is a significant risk of overheating. Another factor that can cause overheating is a faulty cooling system. One of the most common symptoms of a CVT transmission issue is a burning smell emanating from inside the car.
- The Pulley-based
- The Toroidal
- The Ratcheting
- The Hydrostatic/Hydraulic
- The Electrical
- The Cone
- The Epicyclic
- A friction-disk transmission
- The Magnetic
How Does a CVT Transmission Operate?
How Thing Works says that understanding a manual and a conventional automatic is necessary to comprehend how a CVT functions. A manual transmission has a fixed number of gears, and the driver chooses the appropriate gearing.
Although an automatic vehicle likewise has a fixed number of gears, it uses a hydraulic system that senses pressure from the environment to choose the appropriate gear without the driver’s involvement.
The only similarity between a CVT and an automatic is that neither one requires the driver’s input. There are no gears in a CVT. It has two pulleys in its place.
The engine is connected to one pulley, while the wheels are connected to the other. The two pulleys are connected by a flexible belt.
Depending on how much power the vehicle requires, the breadth of the pulleys varies. One pulley shrinks as the other one enlarges.
In contrast to the automatic, which has a fixed number of gears, the pulleys, and the belt can give an endless number of gear ratios because neither is fixed.
Not every CVT is made equal. The most typical form is pulley-based, but there are other varieties as well, such as the Toroidal CVT, which achieves the same result as pulleys by combining rotating discs with power rollers.
Pumps are used in the hydrostatic CVT to regulate fluid flow, which causes a rotational motion.
Which Autos Have CVT Transmissions?
Compared to their European and American rivals, Japanese automakers seem to favor CVT systems more.
That is not to imply that CVT automotive systems have not managed to gain entry into the larger automotive sector. Particularly due to the fuel economy they provide.
Toroidal CVT was used in the Nissan Cedric (Y34) by Yones. Not all CVTs are created equal. Although pulley-based systems are the most prevalent, there are other types as well, such as the Toroidal CVT, which accomplishes the same goal as pulleys by mixing revolving discs with power rollers. The hydrostatic CVT uses pumps to control fluid flow, which generates rotating motion.
Because CVT transmissions are frequently paired with hybrid powertrains, they also feature trustworthy gears that provide quick acceleration.
By checking the vehicle model on the manufacturer’s website and the car’s literature, you can determine that the majority of automobiles use a CVT system.
Several automobiles and SUVs made by Honda, Subaru, and Nissan include CVT technology. These are a few of them.
- The Honda Jazz
- The Lexus RC
- The Honda CR-V
A CVT Transmission: What are Its Benefits and Drawbacks?
You need to be aware of the benefits and drawbacks of CVT systems, just like with any other automobile system.
The Benefits of a CVT Transmission
1. Fuel Efficiency
Because CVTs assure fuel efficiency, modern hybrid automobiles with hybrid powertrains take advantage of them. Midsized sedans with CVT systems, which include certain conventional gas versions, can achieve up to a 38mpg rating, or miles per gallon of fuel.
2. Driving Uphill Is Simpler
It can be difficult to choose the proper gear ratio for the driver when driving a car with a standard gearbox system. It differs from a CVT, which can instantly determine and apply the best ratio.
3. Quick Acceleration
Given that they identify and use the appropriate gear ratio for the drive, whether it is a freeway passing maneuver or an off-the-line circumstance, CVT systems provide quick acceleration.
4. Improved Road Experience
CVT transmissions provide a better driving experience. Finding the ideal ratio enables the car’s engine to seamlessly provide power without the need for abrupt shifts. Your driving experience is substantially enhanced because the engine of the automobile operates consistently across the rpm range.
The Drawbacks of a CVT Transmission
1. It Is Expensive
Comparatively speaking, CVT transmission systems are more expensive. Furthermore, CVT systems are significantly more expensive than their rivals when it comes to repairing and replacement costs.
2. Unsuitable for High-Performance Environments
In CVT systems, the engines are not designed to handle more horsepower.
A typical car engine by Carolla / CC BY-SA 3.0. The clutch that normally goes with CVTs is located in the middle of the transmission and the engine. As you press the gas pedal, the clutch should progressively engage the engine and transmission for a smooth takeoff. If you experience problems such as jerky starting, lurching forward, and delayed engagement, the CVT clutch may be to blame. The problem can be resolved by only reprogramming the clutch after changing the gearbox fluid.
Which are the Common CVT Transmission Problems and Symptoms?
The issue with CVT transmission problems and symptoms is that many of them are difficult to pinpoint. Many issues may be indicated by certain symptoms.
This article just serves as a general overview of CVT transmission problems; nonetheless, each of these issues requires a professional diagnosis.
There is a substantial risk of overheating because CVT systems work with two pulleys and provide an infinite number of gear ratios. Overheating might also be brought on by a defective cooling system. A burning odor coming from within the automobile is one of the more typical signs of CVT transmission problems.
1. Slipping, Jerking, and Grinding
You are correct to take action and begin the process of identifying the problem if you feel that your CVT transmission is sliding. The transmission may be experiencing severe structural problems or fluid concerns if it is slipping excessively.
Lack of lubrication may result from insufficient transmission fluid, which is necessary for the continuous adjustment of the CVT pulleys, belts, and chains.
If the transmission fluid is worn out, the same thing could transpire. While a certain amount of CVT transmission sliding is expected, you will notice it when it interferes with your normal driving habits.
There is still no clear explanation for what is wrong when you hear a grinding noise coming from a CVT transmission; it remains a mystery.
Any form of grinding in the CVT transmission, according to a Honda dealership we spoke with here in Germany, is an indication of worn-out internal components.
However, in most situations, this occurs on high-mileage vehicles where a transmission replacement is to be expected. They did mention that the grinding noises might be alleviated with a shorter transmission fluid interval.
Any CVT transmission that jerks lurches, or accelerates abruptly should raise major red flags. Most often, there are issues with either too little or worn-out or tainted transmission fluid, or the CVT needs to be reprogrammed.
A certain amount of jerking is to be expected when the CVT switches between the “high” and “low” “gears,” according to several accounts we have found. Many people assert that some shaking at low speeds are usual both online and in dealerships.
2. Issues with the Control Module
The CVT has a TCM, or transmission control module, just like every other automatic transmission. This module compiles all the data from your car’s different sensors and decides how the transmission should respond.
You can notice abrupt changes in the behavior of your CVT transmission if the transmission control module a malfunction. There could be a delay in engagement, excessive gearbox slippage, and a variety of other symptoms.
A car engine by Yones / CC BY-SA 3.0. Better driving performance is delivered with CVT transmissions. The engine of the car can deliver power smoothly without the need for abrupt shifts by locating the optimal ratio. Because the car’s engine runs consistently over the rpm range, your driving experience is much improved. The engines used in CVT systems are not built to handle greater horsepower.
When these symptoms appear abruptly and without any past issues, you can figure out if your transmission control module is to blame. The CVT will progressively sustain structural and mechanical degradation, but electronic issues typically manifest right away.
3. When Driving, the Car Produces Whining, Clunking, or Rattling Noises
The CVT transmission should not make any strange noises of any kind. Sometimes, it may simply be a matter of using the incorrect transmission fluid or requiring new transmission fluid.
However, we were informed that many CVTs that are emitting strange noises are experiencing issues with one of the internal bearings.
First, a skilled mechanic will rule out any additional probable causes of strange noises, such as worn wheel bearings, suspension issues, and brake system issues. All of those are significantly less expensive to fix and are frequently mistaken for transmission issues.
4. Issues with the Transmission Fluid
The most common cause of CVT transmission failure is old, worn-out transmission fluid. We must emphasize this.
The majority of the CVT issues and symptoms we’re describing today are brought on by low CVT transmission fluid levels, worn-out CVT transmission fluid, or using incorrect CVT transmission fluid.
A healthy and proper volume of transmission fluid, just as in any type of transmission, avoids mechanical harm to the transmission by lubricating all moving parts and keeping them cool at the same time.
Ensure that the fluid in your CVT transmission is changed at the manufacturer’s recommended intervals and that your CVT transmission is periodically checked for any leaks.
Since it has demonstrated to have a great deal of promise in maintaining the long-term health of your CVT, many owners choose to reduce the time between transmission fluid replacements.
5. Issues with Overheating
Automatic gearboxes of all types are extremely sensitive to overheating. The CVT transmission is no different.
Heavy towing, for instance, might cause overheating. It can also happen when there isn’t enough transmission fluid or when the fluid is worn out. It can also happen if an oil pump malfunction impairs the circulation of the transmission fluid.
If your CVT gearbox is overheating, your car’s dashboard should sound an alarm. Make sure to stop your automobile as quickly as you can if this does occur.
You can resume driving as soon as your CVT gearbox has cooled down if the overheating was brought on by traffic circumstances (severe heat and protracted stop-and-go traffic can overheat the CVT).
The CVT transmission is undoubtedly malfunctioning if the overheated transmission warning message repeatedly appears. If so, the vehicle ought to drive directly to the repair shop.
Transmission fluid by Hymn62 / CC BY-SA 4.0. Transmission fluid that is too old or worn out is the main reason for CVT transmission failure. This needs to be emphasized. Low CVT transmission fluid levels, worn-out CVT transmission fluid, or utilizing the wrong CVT transmission fluid are the main causes of CVT problems and symptoms. Just like in any type of transmission, a healthy and proper level of transmission fluid prevents mechanical damage to the transmission by lubricating all moving parts and keeping them cool at the same time.
6. Due to Issues with the CVT Transmission, the Check Engine Light Comes On
A special “Check CVT transmission” dashboard warning light will be present in some CVT-equipped cars.
However, the “Check Engine” warning light will typically illuminate, and it won’t be until after proper diagnostics have been carried out that you realize the problem is with the internals of the CVT transmission.
To signal a transmission issue, some CVT gearboxes will additionally flash one or all of the gear selector lever lights.
7. The Multi-Plate Metallic Belt or Chain Often Slips Off
A sufficient amount of force must be applied to the metallic multi-plate chain or belt to prevent sliding on the pulleys controlling the gear ratio. Although a certain amount of slide is acceptable and to be expected from the manufacturer, excessive slip is a sign of major transmission damage.
8. Issues with the Flywheel
Similar to the flywheel or torque converter found in a typical hydraulic automatic transmission, CVT transmissions have both.
There have been several reports of flywheel issues with CVT transmissions, and dealerships have advised car owners to just replace the CVT gearbox as a whole without even considering the flywheel.
The owner of a Honda Insight was set to replace the CVT transmission entirely for $4800 in this forum topic, but the malfunctioning component was the CVT flywheel.
However, there are typically no fault codes when using diagnostic tools, which frequently leads dealerships to believe that there is a structural issue with the CVT transmission and that a replacement is required. Symptoms of a defective CVT flywheel can vary, including slipping, juddering, and other problems.
9. CVT Clutch Issues and Signs
The clutch that typically accompanies CVTs sits between the engine and the transmission. The clutch should gradually engage the engine and transmission as you depress the gas pedal, resulting in a smooth takeoff.
The CVT clutch may be at fault if you have issues like jerky starting, lurching forward, and delayed engagement. According to this forum thread, in some circumstances, simply reprogramming the clutch following a transmission fluid change can solve the issue.
How Can You “Test Drive” a CVT Transmission Equipped Vehicle?
Despite all the positive aspects of the car you want to buy, particularly its exceptional fuel efficiency, CVTs have a price that needs to be carefully weighed. The primary drawback of CVT transmissions is their high price.
When a CVT malfunctions, a common replacement can run anywhere from $4,000 to $8,000. You’ll note that I said, “when they fail.” The CVT transmission won’t survive as long as a standard automatic transmission.
The typical lifespan of these machines is 150 000 miles or less.
The fact that they must be replaced 90% of the time when they fail is even more crucial to remember.
This is because replacement parts are very expensive, occasionally impossible to source, and frequently suffer from such severe damage that they are not even worth trying to repair.
Automatic transmission by Leoiii6382 / CC BY 4.0. CVT transmissions have both, much like the flywheel or torque converter found in a typical hydraulic automatic transmission. Many CVT transmission flywheel problems have been reported, and dealerships have encouraged car owners to just replace the CVT gearbox as a complete without even thinking about the flywheel.
The CVT’s inability to handle the horsepower that an automatic or manual transmission can handle is another drawback. The CVT unit is therefore never employed in high-performance circumstances.
But, if you decide to buy a used CVT, pay attention to these signs when you test-drive the vehicle:
1. Pay Attention to Slow Shifting
With a CVT transmission, you don’t need to change from first to second gear, but you do need to switch between the park, drive, and reverse to operate your automobile properly. A defective CVT transmission may be evident if it takes the transmission more than a few seconds to shift.
2. Keep an Ear Out for Any Unusual Transmission Sounds
Although CVT transmissions tend to be noisier and produce more noise than their conventional manual or automatic equivalents, they shouldn’t be so noisy as to make it normal for drivers to hear humming and whining.
Your car may jerk or make excessive noises while you accelerate, which are signs that the CVT transmission is malfunctioning.
3. Pay Attention to How the Transmission Is Slipping
Your car should accelerate smoothly, seamlessly, and continuously when you press the accelerator. A damaged or defective CVT transmission will exhibit acceleration slippage and power loss while you are driving.
4. Shifting That Jerks or Uneven Shifts When the Vehicle Accelerates
This might happen while your automobile accelerates or shifts gears. Shifting shouldn’t ever cause the car to jerk, therefore if it does, the CVT transmission is malfunctioning.
5. RPM Fluctuations are a Sign of a Malfunctioning CVT Transmission
If the engine RPM varies while you are traveling at a constant pace, even though the CVT gearbox should remain smooth and constant, there is probably something wrong with your vehicle.
How Much Does a CVT Transmission Replacement Cost?
The location, the repair facility, as well as the make and model of the vehicle in question, all affect the price of a CVT repair. However, replacing a CVT transmission typically costs between $3,000 and $5,000. In some circumstances, the price can go up.
Are CVT Transmissions More Problematic?
That is concerning the car owner’s design and upkeep. Older CVT systems do not last as long as conventional transmission designs because of reliability and durability difficulties. Nonetheless, when properly maintained, several of the upgraded CVT designs outlive their conventional equivalents.
How Come CVT Transmissions are So Bad?
The same idea behind CVT transmissions that makes them so fantastic also turns out to be a problem. Because the system’s parts move often, CVT transmissions are prone to malfunction.
Because of the constant motion, CVTs are more likely to experience wear and tear and malfunction than other transmission systems. Yet, automakers are developing designs to reduce CVT transmission reliability difficulties.
What Is the Lifespan of a CVT Transmission?
The design of the CVT system and the maintenance habits of the vehicle owner have a big impact on how long a CVT transmission lasts. In any case, the typical CVT system has a lifespan of up to 100,000 kilometers. Recent CVT models have been known to last up to 300,000 miles.
The Conclusion
The adoption of CVT transmissions has several advantages for car owners. A CVT transmission vehicle offers a better driving experience, increased fuel efficiency, and extremely rapid acceleration. But, you must be aware of the issues with CVT transmissions that arise while employing such transmissions.
In addition to answering some frequently asked questions concerning CVT designs, the essay discussed some of the more prevalent issues that CVT systems face.
At this time, hopefully, you should know more about CVT issues with specific vehicles, such as the 2021 Toyota Corolla CVT issues.
It is challenging to discuss CVT transmissions generally since, as we discovered during our study for this post, many CVT transmission manufacturers provide various fixes for particular inbuilt CVT flaws.
And while a CVT gearbox made by business A might be faultless, a second CVT made by company B might employ the same basic architecture but yet have several issues.
It is because of this that CVT transmissions have a negative reputation. They assume that this is standard after hearing those horrifying tales of owners having to repair entire transmissions for $3,000 to $6,000. We firmly believe it isn’t, too.

A continuously variable transmission by Hatsukari715

Jim Wicks is the founder of MotorVehicleHQ. With over two decades of experience in the automotive industry and a degree in Automotive Technology, Jim is a certified car expert who has worked in various roles ranging from a mechanic, car dealership manager, to a racing car driver. He has owned more than 20 cars over the past 15 years. Ask him about any vehicle you see on the road and he can tell you the make, model and year. He loves the aesthetics of all things cars, and keeps his vehicles in pristine condition.
In his free time, Jim enjoys getting his hands dirty under the hood of a classic car or taking long drives along the country roads. His favorite car? A 1967 Shelby GT500, a true classic that, according to Jim, “represents the pure essence of American muscle.”