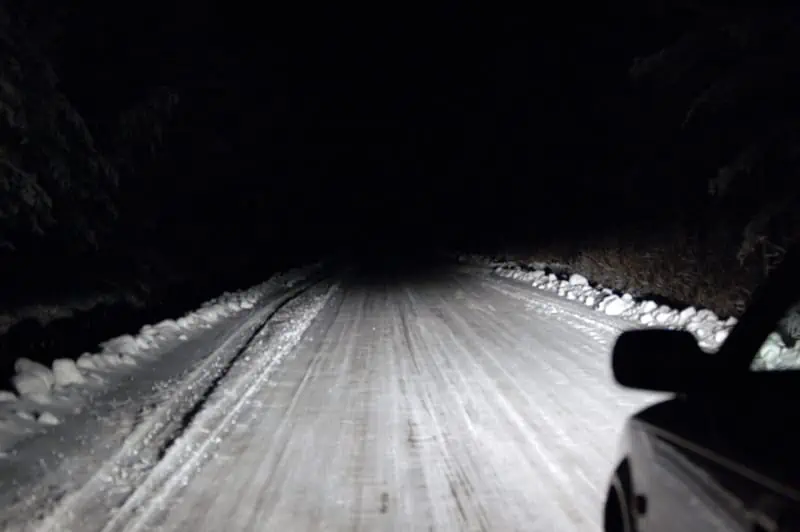
The ability to see where you’re going and the ability to be seen by other road users are the two main issues that drivers face when visibility is limited, whether due to weather or low light.
High beam and low beam headlights are the two settings for car headlights. What are the functions of these two settings, and when ought each set to be used?
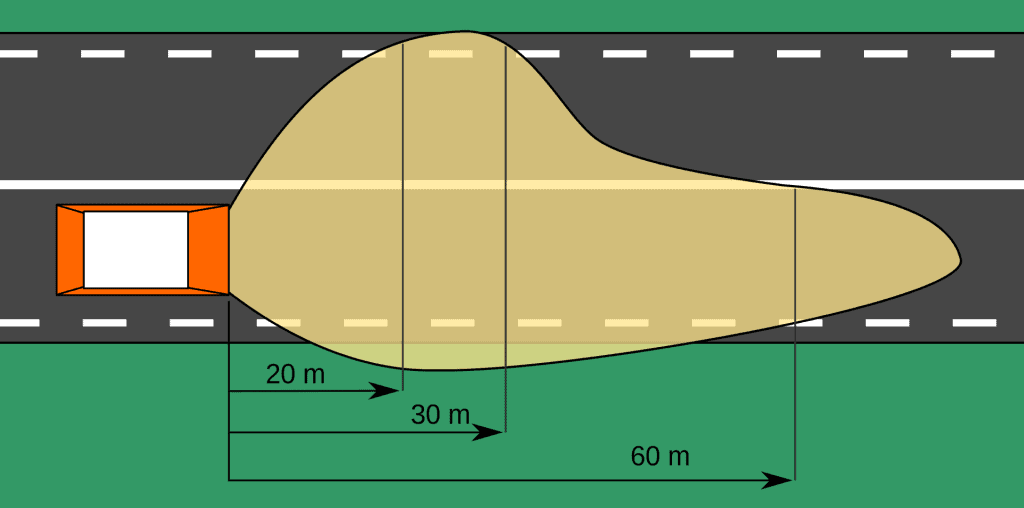
High beams illuminate the road ahead farther and more evenly since they are brighter and project a symmetrical beam. The road ahead is illuminated across a smaller area by the low beam’s asymmetrical beam. High beams are for driving on dark highways; low beams are for city driving where there are lamps.
Since the days of an oil lamp in a lantern with a reflector, headlights for motor vehicles have advanced significantly, but with that progress comes a need to comprehend how the contemporary headlight functions.
Although there are many various kinds of headlights, the primary headlights always perform the same basic duties. The vehicle must have both low beam headlights and high beam headlights to be roadworthy. Let’s examine these two aspects, their functionality, and their appropriate applications.
What Defines High Beam Headlights from Low Beam Headlights?
Depending on where you’re from, the high beam and the low beam headlights may have various names. The terms main beams, full beams, brights, and driving beams are occasionally used to describe high beams.
A low beam illumination of the road by Scoo. / CC BY-SA 2.5. Low beam headlights should be utilized when traveling in cities when the road is well-lighted by lamps. Additionally, low beam headlights should be used when approaching the car in front of you and when an incoming car is visible. For poor-visibility conditions like fog, rain, smoke, dust, or snow, low beam headlights must be used.
A low beam is also referred to as a meeting beam, dims, passing beam, or dipping beam.
Many individuals think that the difference in brightness between the high and low beam settings on car headlights is all that matters. The distinction between the two situations is somewhat more nuanced than this.
The following are the primary distinctions between high beam and low beam headlights.
1. The Brightness
Significantly more light is produced by the high beam than by the low beam headlights.
2. The Distance
When compared to high beams, a high beam illuminates the road for a greater distance, giving you more visibility. Low beam headlights cast a narrower light on the road in front of you.
3. Viewing Area
The high beam, which lights up more of the side of the road than the space in front, illuminates a narrower arc than the low beam. High beams have a narrower beam that illuminates farther away but less peripherally.
4. The Symmetrical Illumination
High beams illuminate the road in front of you symmetrically, which illuminates both sides of the road as well as the distance in front of you.
Low beam headlights asymmetrically illuminate the road, illuminating both the edge of the road on your side and the road in your lane as well as the side facing oncoming traffic.
The two types of headlight beams differ primarily in these ways, but you still need to be aware of when to utilize each type of beam on the road.
Your decision over which beam to employ will depend on certain circumstances and driving conditions. Your choice of the beam should take into account road safety, both for your driving safety and the safety of other road users.
When Should I Use Low Beam Headlights?
A low beam is an uneven, low-intensity, dipped setting on a car’s headlights. It is crucial to know when to utilize this setting to maximize your visibility and the safety of other drivers.
Asymmetrical low beam illumination of road surface by cflm / CC BY-SA 4.0. Low beam headlights are the best choice to use when there is poor visibility on the road due to rain, fog, smoke, dust, or snow. Since they will illuminate the road at a lower level without reflecting the beam at you, low beam headlights are the better headlight setting under these conditions.
For city driving where the road is well-lit by lamps, low beam headlights should be used. Additionally, while approaching a vehicle in front of you and when an approaching vehicle is seen, low beam headlights should be employed. The use of low beam headlights is necessary for low-visibility situations like fog, rain, smoke, dust, or snow.
1. At the Urban Streets
Because the road and the verge are well-lit overall by city streets with streetlights, low beam headlights are adequate in these circumstances. Your visibility to other drivers is more of a goal of the low beam headlights.
There is typically enough ambient light on the streets, even on dimly lit metropolitan streets, to make low beam headlights adequate for driving safely. High beams may occasionally be needed for increased visibility on darker roadways, but they should only be used when necessary.
2. Approaching a Different Car from Behind
Many novice drivers overlook the fact that high beams approaching from behind will reflect in the rearview mirror of the automobile in front of you, dazzle or blind the driver of that car. Always switch to low beam headlights if you are following another car while your lights are on high beam.
3. Approaching Traffic
A high beam will shine straight in their eyes as traffic in the opposing lane moves toward you, making it challenging for them to see clearly.
When oncoming traffic is close by, you should switch to your low beam headlights, which will dimmer your lights and direct the beam away from the approaching car.
4. Circumstances with Poor Visibility
When there is poor visibility on the road due to rain, fog, smoke, dust, or snow, low beam headlights are the ideal option to utilize. The low beam headlights are the better headlight setting in these circumstances since they will illuminate the road at a lower level without reflecting the beam at you.
When Should I Use the High Beam Headlights?
A high beam is a setting on a car’s headlights that is bright, symmetrical, and high intensity. Knowing when to use this option is crucial to giving you a clear perspective of the road ahead without compromising other drivers’ vision or safety.
For driving on rural or country roads or on sections of the highway that are not adequately illuminated, high beams should be used. They can also be used sparingly when driving in cities with little or no lighting and dark roads. The safety of other drivers should always be taken into account when using high beams.
A high beam illumination of the road by Scoo / CC BY-SA 2.5. High beams are brighter and project a symmetrical beam, which illuminates the road ahead farther and more evenly. The asymmetrical beam of the low beam illuminates a lesser area of the road ahead. For driving on dark highways, use high beams; for driving in cities with lighting, use low beams.
Your headlights’ high beam setting is designed to be used on dark roads with no streetlights and scant ambient lighting from nearby buildings and residences. You can see dark roads or highways well in the distance when the beam is set high.
You can see the road ahead more clearly with a high beam, including any obstructions, the state of the road’s surface, and other potential hazards. The high beam illuminates a large area up ahead, giving you plenty of time to react to any risks that may be there.
When Should I Avoid Using High Beam Headlights?
Even though the road is dark and poorly lit, there are some situations on the road where using a high beam is inappropriate.
When approaching from behind other vehicles in front of you or from the opposite lane, you shouldn’t use your high lights. Additionally, high beams should not be used when there is poor visibility on the road because of fog, rain, snow, dust, or smoke.
You must switch to low beam headlights if you are approaching from behind slower-moving vehicles in front of you. The vehicle in front may be dazzled by a high beam that reflects in their rearview mirror and causes them to lose visibility, which could lead to an accident.
You must switch to low beam headlights while approaching oncoming traffic when driving on a dark road to prevent briefly blinding the driver with your high beams.
Using high lights under poor road visibility conditions that cause airborne particles is not recommended. Rain, mist or fog, snow, dust, and smoke are some examples of these situations.
One might assume that the high beam would be able to see through airborne particles better than the low beam headlights and provide improved visibility, but this is untrue.
The airborne particles disperse the intense beam, and some of them will reflect off it at you. You become bright as a result, which lowers your visibility. In these circumstances, you have superior vision thanks to the low beam headlights’ lower level illumination, which reflects less light in your direction.
How to Utilize High Beam Headlights Effectively
High beam settings must be utilized sensibly and with consideration for other road users’ safety. When using high lights while driving, there are some general dos and don’ts.
You can typically see the glow of incoming traffic’s headlights as you get closer to a hill or rise’s summit. If your headlights are on a high beam, turn them to a low beam so that you won’t blind the other motorist when you or the approaching car crests the hill.
Similarly, you may see the glow of incoming traffic’s headlights as they approach a tight bend in the road. Before rounding the curve, dim your headlights to prevent momentarily blinding the approaching car.
Symmetrical high beam illumination of road surface by Ruizo / CC BY-SA 3.0. Headlights that are bright, symmetrical, and intense are known as high beams. To give you a clear view of the road ahead without compromising other drivers’ eyesight or safety, you must know when to use this option. High beams should be utilized when driving on rural or country roads as well as on portions of the highway that are inadequately lit.
When coming from behind and approaching vehicles in your traffic lane, always switch your headlights from high to low beams. By doing this, you can prevent your high beams from blinding the driver in front of you when they reflect in their rearview mirror.
The Symbol of High Beam Vs. Low Beam Headlights
Every car has a set of symbols that, along with indicators on the controls for high and low beams, show what mode the headlights are now in.
When high beams are engaged, the dashboard’s high beam indicator will turn on. This emblem depicts a headlight with several horizontal lines extending from the light’s front. When the high beams are on, a blue light will shine on this dash sign.
The same symbol will be used as the high beam indicator on the light controls. The same headlight emblem serves as the low beam indicator, but for low beam headlights, the lines extending from the front of the headlamp are pointed downward.
The Workings of Low Beam Headlights
Low beam headlights operate by reducing the beam’s intensity and dipping them at a shallower angle. Additionally, the beam has been altered to be asymmetrical so that it does not reflect strongly into the lane for approaching traffic while still lighting up your driving lane.
The low beam headlights effectively place the beam down, away from the oncoming traffic lane, and forward. The low beam headlights will be oriented left in nations where drivers travel on the left side of the road.
In North America, which is governed by the SAE standard, the laws governing how much light from the low beam headlights cross into the oncoming lane are less stringent. The ECE laws, which control international standards, are stricter regarding the amount of light entering the opposite traffic lane.
The Workings of High Beam Headlights
Your headlights’ beam is raised to shine farther into the night, its intensity is enhanced, and it illuminates the entire road, including the lane for oncoming traffic, when the high beam setting is selected.
Early cars had a manual footswitch on the floor that was used to turn on the high beam and low beam headlights. The controls have shifted from being foot-controlled to being electronic and hand-controlled. Frequently, the steering column control used to turn on and off the lights also controls the high/low beam headlights.
Many cars feature a temporary high beam on the same control that turns them on for a brief period when you pull the lever in your direction and turns them off when you let go.
Projector headlamps on a Mercedes Benz by Premnath Kudva / CC BY-SA 3.0. The high beam setting on your headlights is intended to be utilized on dark roads with no streetlights and little ambient lighting from surrounding structures and homes. When the beam is set high, dark roads or highways can be seen clearly in the distance. A high beam makes it easier to see the road ahead, including any impediments, the condition of the surface, and other potential dangers.
Do High and Low Beam Headlights Require Different Bulbs?
The technology that your car’s manufacturer has chosen as a standard and the age of your automobile will determine the high beam and low beam headlights mechanism that is utilized in your vehicle.
Some cars employ a two-bulb system that uses an HID bulb for the high beam and a halogen bulb for the low beam headlights. Due to the various connecting types, the halogen and HID bulbs cannot be switched. One bulb with two filaments, one for the high beam and the other for the low beam, is used in some designs.
Some automakers are using LED headlights, and these lights are becoming more and more well-liked due to their low energy consumption for brightness levels comparable to those of other bulb types.
Laws for the Use of High Beams
Many drivers are unaware of the traffic regulations governing the usage of highlights. According to traffic regulations, if you are driving with your high beam on, you must change to your low beam headlights when you are 500 feet or less from an approaching vehicle.
It is also against the law to approach a car from behind while using your high beams. When you are 200 to 300 feet or less from the car in front of you, the law mandates that you change from your high beam to your low beam headlights.
The Benefits of Using High Beam and Low Beam Headlights
Both approaches have advantages depending on the location, light, and weather.
1. Benefits of Low Beam Headlights
- Fewer mishaps The car in front of you and oncoming traffic can both be kept safer by using low lights.
- Perfect for climatic extremes. You should utilize low beam headlights to improve your road visibility whether it is raining, foggy, or snowing. The motorist won’t become blinded by light particles that bounce off of cloud particles.
- The refined mode of transport. The beam won’t strain the eyes of cars, cyclists, or pedestrians.
HID projector low beam headlamp by Ford Motor Company / CC BY 2.0. Currently, left-angled low-beam headlights are used in nations having left-hand traffic. In contrast, low-beam lights tilt to the right in nations with right-hand traffic. Your lights won’t blind drivers who are moving in the opposite direction from you if you do it this way. Some countries, like Canada, have mandated daytime running lights for all automobiles.
2. Benefits of High Beam Headlights
- Improved visibility High beams are ideal in dimly lit regions or on desolate roadways since they project light more intensely.
- Ability to serve as a signaling tool. To alert onlookers to the presence of the vehicle or to indicate a right-of-way, we can flash our highlights.
- Noise pollution reduction. Noise pollution can be decreased at night by utilizing your high beams instead of your horn.
Safety Precautions
To ensure the increased safety of drivers on the road, certain nations have taken additional steps.
For instance, countries with left-hand traffic now use low-beam headlights that slant to the left. In contrast, low-beam lights in countries with right-hand traffic slant to the right. In this manner, your lights won’t blind motorists who are traveling in the opposite direction from you.
Some nations, such as Canada, have made Daytime Running Lights a requirement for every vehicle. When it comes to improving vision during the day, DRLs are extremely important. Increased visibility dramatically reduces the likelihood of traffic accidents.
One should keep in mind, though, that DRLs do not turn on the taillights. In severe weather when the road conditions and visibility are poor, it is advised to turn on low beam headlights.
Changing from Low-Beam to High-Beam: A Guide
The processes used by various makes and models of cars to transition from low to high beam headlights and back again are different.
The mechanism is typically a part of the lever adjacent to the steering wheel that is used to turn the on and off the headlights. Alternatively, a tiny button on the driver’s floor can be used to turn on the high lights.
Turn on the headlights, then depress the lever with your hand or depress the floor button with your foot to switch from low to high beam.
Simply repeat this process to change back. Some versions with lever-activated high beams headlights allow you to press the lever in one direction to briefly flash them before pressing it in the opposite direction to turn them permanently on.
Audi Matrix Laser headlamp by Robert Basic / CC BY-SA 2.0. If you are driving with your high beam on, you are required to switch to your low beam headlights when you are 500 feet or less from an oncoming vehicle, according to traffic regulations. Using your highlights when approaching a car from behind is likewise illegal. The law requires you to switch from your high beam to your low beam headlights when you are 200 to 300 feet or less from the vehicle in front of you.
Systems for Dual-Beam Headlights
All automobiles and trucks have a low beam and a high beam function, but some have single beam systems that require two separate bulbs for each beam while others have dual beam systems that just need one bulb for both.
One pair of bulbs will suffice for drivers of vehicles equipped with dual beam systems to upgrade (or replace) both the low and high beams. Dual-beam bulbs use more electricity and are often a little more expensive than single-beam lamps.
The Conclusion
In conclusion, low-beam headlights are most frequently used when driving in cities and in weather conditions like smoke, rain, fog, dust, or snow that make it difficult to see the road ahead.
To protect the eyesight of drivers approaching that lane of traffic, low beam headlights divert the headlights’ beam downward and away from it.
When driving in locations where headlights are required to be on during daytime hours, a low beam is the best setting to utilize. This makes you more noticeable on the road, especially during the day.
High beams are designed to be used on dark routes, including rural or interstate highways without streetlight lighting. High beams can harm other road users’ safety, vision, and ability to drive.
As a result, you must turn off your high beam when you are 500 feet or less from oncoming traffic and 200 to 300 feet or less from oncoming traffic in your driving lane.
Being a safe, thoughtful road user requires understanding the effects of high and low lights as well as the proper situations in which to utilize each level.

HID projector low beam headlamp by Ford Motor Company / CC BY 2.0

Jim Wicks is the founder of MotorVehicleHQ. With over two decades of experience in the automotive industry and a degree in Automotive Technology, Jim is a certified car expert who has worked in various roles ranging from a mechanic, car dealership manager, to a racing car driver. He has owned more than 20 cars over the past 15 years. Ask him about any vehicle you see on the road and he can tell you the make, model and year. He loves the aesthetics of all things cars, and keeps his vehicles in pristine condition.
In his free time, Jim enjoys getting his hands dirty under the hood of a classic car or taking long drives along the country roads. His favorite car? A 1967 Shelby GT500, a true classic that, according to Jim, “represents the pure essence of American muscle.”