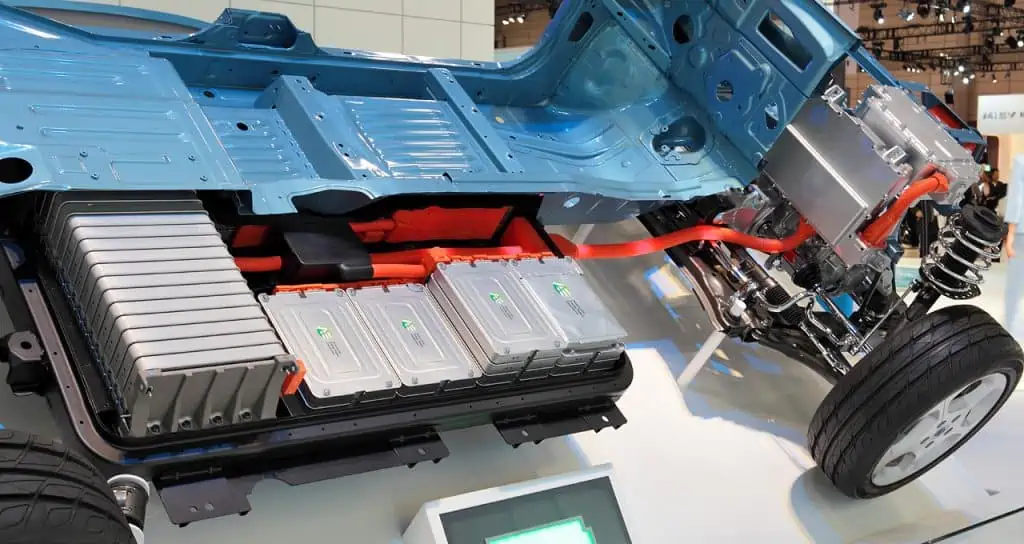
We are aware of the idea that all mechanical and electrical devices rely on energy to function. All mechanical and electrical devices require power, that much is true. It receives power from a source for effective operation.
These energy sources might include fuel, batteries, electricity, geothermal energy, etc. But one item adds a layer of complexity. A vehicle. What kind of energy does a vehicle run on specifically?
A vehicle uses a variety of energy sources, including gasoline, CNG, diesel, electricity, etc. It still needs a battery even if it can run on all of these different types of energy. Then additional queries come up. How is the battery? Is a vehicle battery AC or DC?
You could have left here with more questions than answers, then. If a car relies on gasoline for operation, what would be the point of a battery? A vehicle battery is a crucial source of power for the ignition process.
The battery aids in jump-starting the vehicle’s engine. Following ignition, the alternator is driven by the engine’s spin, which forces electrical current into a battery where it is stored as chemical energy.
A battery is a crucial part of a vehicle since it not only powers the ignition but also several other functions including lighting up the inside and outside of the vehicle, powering the music system, operating the GPS, supplying electricity for the headlights, and operating the DVD player.
There are two types of batteries: DC batteries and AC batteries. This variance is determined by the electrical need and purpose. In this article, we distinguish between AC and DC and identify which is utilized in vehicles.
What Do AC and DC Mean?
According to your needs and the electrical function of the application, there are two distinct types of batteries. AC and DC technology are the two primary technologies used in the production of vehicle batteries. But how do they differ?
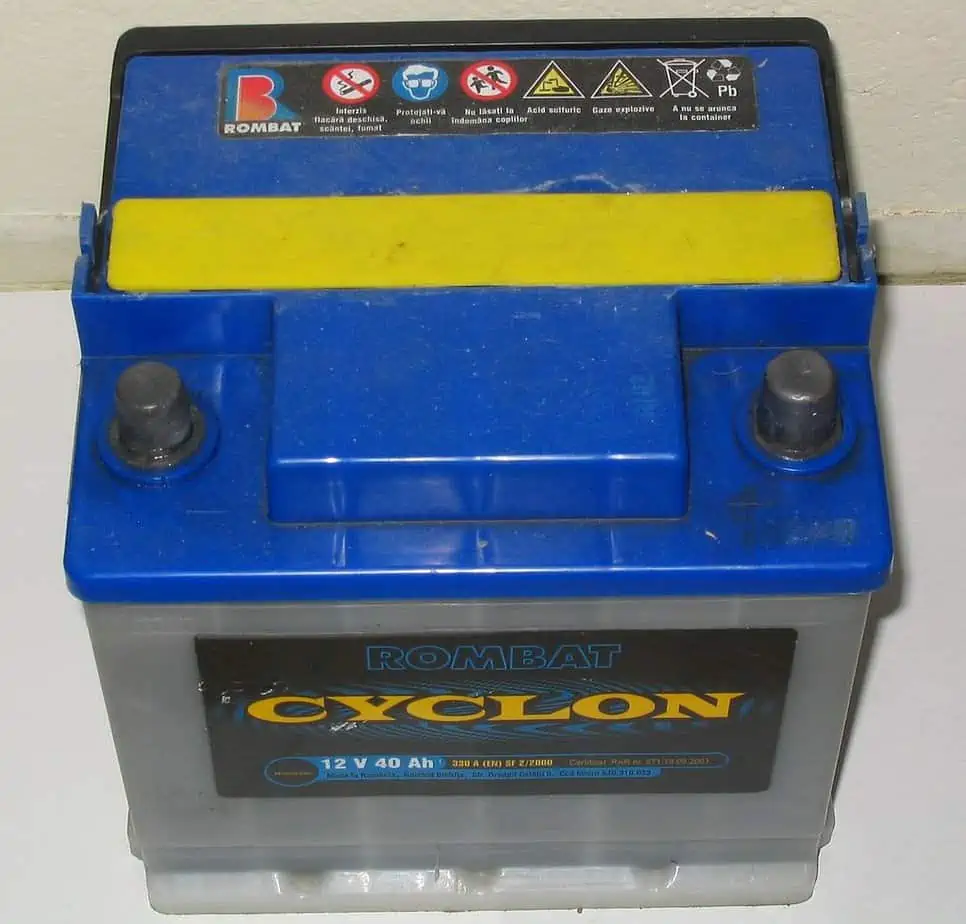
A 12 V, 40 Ah lead-acid car battery. A battery is an essential component of a car since it, not only powers the ignition but also many other features including the interior and exterior lighting, the music system, the GPS, the power for the headlights, and the DVD player.
The Direct Current (DC)
This refers to the movement of electrons in a specific direction. DC power has a voltage that is always positive or negative and has a consistent polarity. A battery generates this kind of current, which can go from the positive to the negative terminal of the battery. Due to its ease of storage, even on a small scale, DC power typically has an advantage over AC power.
According to historical records, Thomas Edison used this kind of current to power his initial transmission system. Small electronic equipment like radios, microwaves, computers, and many more are often powered by DC electricity.
Batteries are the only source of DC power. Through internal chemical processes, a battery may quickly convert chemical energy into electrical energy. Typically, the battery houses these compounds. The battery’s main job is to supply power to other system components.
DC electricity never reverses direction; it only ever goes in one direction. As a result, batteries can transport a lot of power more effectively and for very little money. A battery may also store chemical energy for a very long period without the use of additional converters.
When necessary, it is simple to convert this type of chemical energy into electrical energy. A battery’s energy may easily be shifted from one location to another, making it incredibly portable.
The Alternating Current (AC)
Continuous current flow in varying directions is known as alternating current. Nikola Tesla was the first to use this kind of electricity to power the transmission system he created. There aren’t any AC batteries on the market right now. Only a few DC batteries have converters installed to aid in converting DC power to AC.
The fact that AC power may flow in two distinct directions and can thus transport electrons over very long distances without losing power is one of its key advantages. Batteries with AC converters are more effective energy sources and have the additional advantage of being able to store this energy in a portable device.
Do Batteries Discharge AC or DC Power?
Chemical cells are used in batteries to provide a high electric potential. AC can generate electrical current for powering structures.
Long-distance AC transportation is simpler and more effective. Even AC may be converted into a greater voltage. A lesser current will be present at a greater voltage. Additionally, this lowers power losses. Remember that there is no AC battery once more.
Several DC batteries can produce AC with the use of converters. A DC battery may be controlled to the fullest extent when an AC converter is used with it. DC is utilized in electronics and only flows in one direction.
It can deliver steady DC power in a single direction. Electricity will be supplied with it from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Random direction changes are possible with AC, and to do so, the polarity must also be changed quickly.
A battery will only charge through the half-positive cycle and discharge through the half-negative cycle if an AC source is connected to it. Thus, the answer to the question of whether the vehicle battery is AC or DC is DC. It can discharge entirely without providing any more power, even when it functions perfectly.
It may convert mechanical energy into electrical energy when used in conjunction with alternators. For the vehicle battery to store chemical energy, it aids in its conversion. The AC battery won’t be able to adjust the terminals’ polarity at the same level, which is the cause. Since the average voltage throughout a full cycle is equal to zero, you cannot store AC in a vehicle battery.
A standard car battery may contain between 200 and 225 amp-hours and 12 volts (Ah). Driving can recharge your battery, but don’t expect it to entirely or even almost fully recharge.
Understanding Car Battery Fundamentals
You can locate the several systems that work in concert with one another in a car. The passage of electrons is aided by the power of electricity. There are positive and negative sides to a circuit. These are too tiny to run a motor, yet they still have an electric charge. To power these devices in your vehicle, you need a car battery.
To characterize a car battery, we can state that it has a rechargeable design and supplies electrical flow to the vehicle’s engine. You won’t be able to power the starter, which further aids in starting the motor, without a car battery. A generator that aids in controlling the electrical structures is also present.
If you ever experience problems with your car’s battery, you might wonder what kind of battery you should use. You could be unsure if it is AC or DC. But you must always obtain it per the kind of car.
A Vehicle Battery: Is It AC or DC?
Car batteries are all DC, after all. This is because batteries are unable to hold AC power. There are a few explanations for why a car battery uses DC electricity.
One is that AC electricity often, at least 50 times per second, changes direction. Because of this, it would be practically difficult for a battery to store AC power because the battery would have to switch the polarity of its terminals 50 times each second.
Second, there is no way for AC power to be stored in a battery if an AC source is attached to it. If this happens, the battery will only be able to store AC power during the positive half of its cycle and will discharge it again during the negative half.
To be clear, though, even DC electricity cannot be stored in a battery. Instead, it may be transformed into chemical energy and kept in a vehicle battery for use in the future. As we previously stated, all batteries operate on DC. In other words, a car battery utilizes DC electricity.
However, it should be noted that the remainder of the vehicle can require AC power. DC electricity has to be converted into AC utilizing extra circuitry to function on an AC system.
Through the use of an AC converter, which is installed in vehicles for this specific purpose, AC power may be generated from a DC battery. DC is more often used in low voltage electric vehicle applications.
Since batteries may also be charged using DC power, AC is always converted to DC first when a battery is the main component of the system.
How Do Automotive Batteries Function?
A typical vehicle battery has a capacity of 200 to 225 amp-hours and holds 12 volts (Ah). Driving your car can recharge it, but don’t count on it to totally or even nearly fully recharge your battery.
Additionally, rather than only charging the battery while you’re driving, the majority of the electricity generated by your alternator powers all of the electrical accessories like the audio, turn signals, and headlights.
The alternator in a vehicle works hard to charge everything but the battery.
The conventional battery in your car constantly receives power from the alternator to keep it charged, but it has a lower charging capacity than a high-power deep cycle marine or RV battery. The batteries in RVs are made to be “deep” discharged and recharged as well as to be left idle for extended periods (i.e, storage).
Alternator mounted on a V8 engine. While your car’s conventional battery is continually being charged by the alternator, it has a lesser charging capacity than a high-power deep cycle marine or RV battery.
The amp-hours rating of car batteries is rather low (in comparison to deep cycle marine or RV batteries), they don’t have enough reserve capacity to run many electrical accessories for an extended period, and they only deliver dc voltage, not AC.
For his early electric power transmission systems, Thomas Edison employed direct current. Small electronic devices and appliances including computers, radios, microwaves, and more are powered by DC batteries.
If you’ve been driving your car and the battery has been drained, the alternator will, at best, only deliver 15% of its typical charging capability when it tries to recharge the car battery back up to 12 volts.
Any battery, including a vehicle battery, discharges DC voltage. If you want to make it AC, it needs a few extra circuits.
How Do Automotive Alternators Function?
The pulleys—one for the engine and the other for the alternator itself—are connected to the alternator by a belt, which also makes it possible for additional accessories to operate. In addition to charging the battery, the alternator also supplies electricity for additional electrical equipment like headlights, turn signals, and car stereos.
The alternator typically outputs AC. For usage, this output is instantly changed to DC. In the past, DC generators in vehicles assisted in supplying electricity.
However, as a result of a considerable rise in automotive electrical usage, these DC generators were eventually swapped out for alternators. The alternator could readily provide high power even at low RPM and was more effective at charging.
Produced by the alternator is AC power. It must be converted to DC because AC is rarely utilized in automotive electronics. As a result, the alternator has full-bridge rectifiers placed inside of it that employ four diodes to assist in converting AC to DC. The battery is then used to store the converted DC.
In What Ways are AC and DC Converted?
An electrical component known as a solid-state diode, of which there are several varieties, may convert AC power (alternating current) into a DC generator. Alternately, a transformer/rectifier setup may convert an AC adaptor into DC (low voltage).
A basic semiconductor device called a diode (which generates chemical energy) consists of two “electrodes” made of n- or p-doped silicon, with the cathode serving as the positive terminal. There are three terminals total when two additional electrodes are utilized, one of which is more positive than the cathode and the other of which is less charged.
Cathodes are not negative in any other way; the term “negative” refers to their voltage potential to the ground (0 volts). Lithium-ion batteries also employ these cathodes and diodes. A portable battery unit is another name for this battery (AC or DC). It serves as a low voltage source for a vehicle’s electrical system.
The Benefits of DC Batteries
DC batteries have a lot of advantages. It can mitigate the effects of environmental catastrophes and aid in reducing carbon emissions. The fact that DC batteries can transmit more power over longer distances while ensuring that there will be fewer electrical losses is one of its finest qualities.
It will do it in a way that offers great efficiency even at a lower cost. To stop wear-out caused by specific factors, you can simply swap the battery. The ability of DC batteries to convert chemical energy into mechanical energy is another advantage. It flows in one direction without turning around.
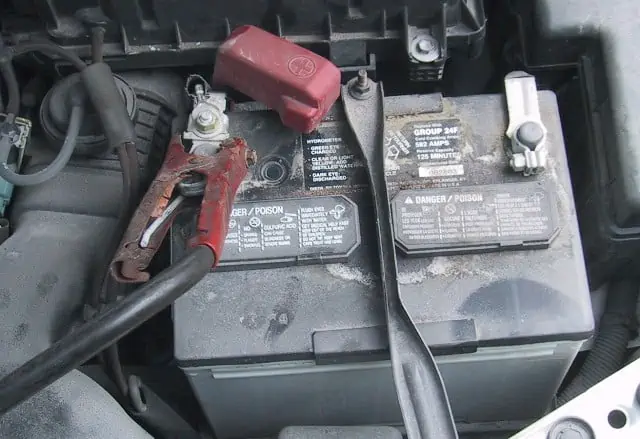
Car alternator dynamo by Piero / CC BY-SA 3.0. When trying to restore the automobile battery to 12 volts after it has been discharged while you have been driving, the alternator will, at best, only provide 15% of its regular charging capacity.
Which Is Superior, DC or AC?
It is essential to list each electrical type’s benefits and drawbacks to better comprehend which is superior. Let’s start by talking about AC power. The first is that AC is efficient in transmitting electricity.
As was already said, high voltage is utilized to maintain a consistent flow of electricity, which also implies that less current travels through the power line, reducing power loss.
Second, AC was advantageous because it provided power generation a chance to succeed. Following its creation, the AC generator was also developed, which led to the development of hydroelectric AC generators, which are still in use today. And this is less complicated than DC’s mechanical generating.
Another benefit of AC is that it doesn’t require the commutators and brushes that DC machines have to produce energy. Tesla received a patent for the first AC induction motor, which was utilized with AC electricity, in the late 1800s.
The manufacturers in the United States produced this breakthrough and made it available. Today, domestic equipment like garbage disposals, electric fans, compressors, and air conditioners are all powered by this engineering achievement. Using DC is also recommended.
Additionally, AC offers greater illumination. In contrast to Thomas Edison’s incandescent bulbs or lights, which run on both AC and DC, more compact fluorescent lights that operate at high voltage are becoming popular nowadays.
The more practical fluorescent lights create an ultraviolet spectrum by using high voltage and gases like mercury vapor and argon.
Alternating electricity is reportedly less costly and more readily available than direct current. Due to these two characteristics, AC is more useful and preferred over DC.
The cost of using AC in vehicles is the other side of the coin. Potential owners of Tesla Model S vehicles have the option to change the charging current from AC to DC. More rapid charging is available, but it is restricted, and car owners must pay an extra $1,500 for it.
Another drawback of AC is that it requires more insulation due to the high voltage needed to deliver fixed power. This in turn makes handling more challenging. Working with AC is riskier than with DC.
Issues with AC generators are another factor. For the straightforward transformation of AC into various voltages, electrons must be run back and forth. This causes magnetic fields to increase and decrease, and it takes a lot of power to do this.
When utilized in submarine cables, AC generators produce the incorrect form of power. Some users would rather transfer DC using another method than AC since AC requires raising substations every 400 miles, which some people find unfeasible.
Due to the necessity for AC generators to produce large currents, AC electricity is also vulnerable to heating and sparking, which might result in fires and electric shock. Aside from the power loss when an AC generator begins and stops each time it is transformed and up to the final transmission from AC to DC, AC generators are also less durable than DC generators.
Electronic transmission lines may be hazardous, particularly when mobile phone users are lured to charge their phones using chargers of poorer quality. Explosions and other dangerous scenarios might occur when the faulty charger warms up.
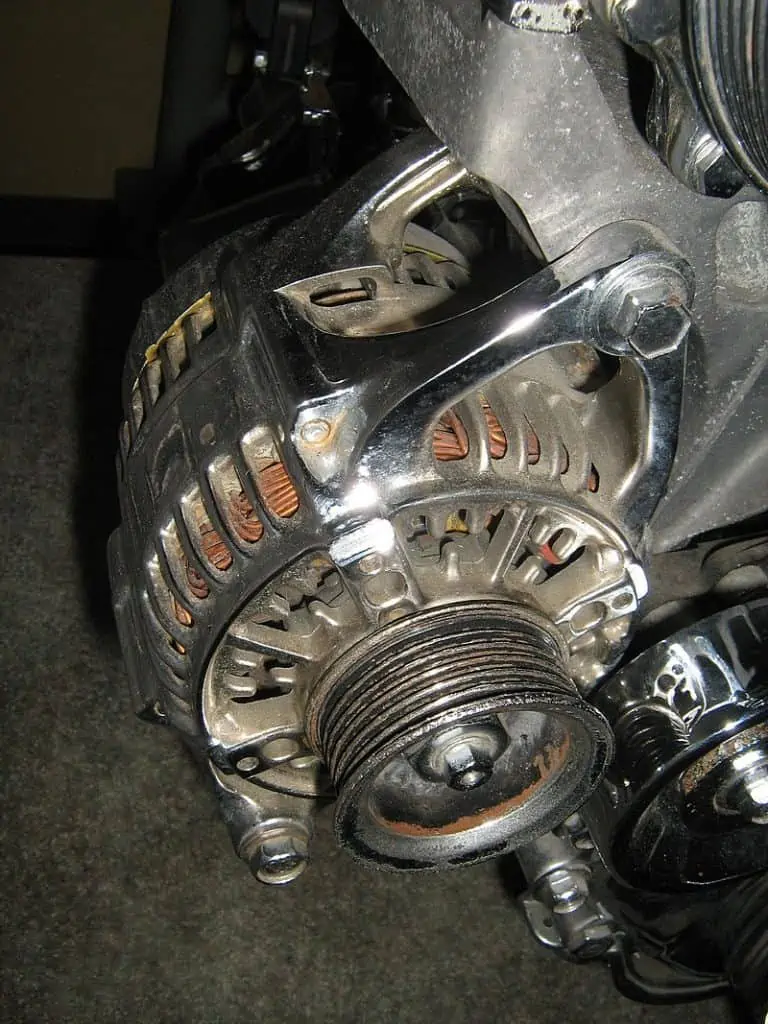
Compact alternator by CZmarlin. The alternator generates AC electricity. Because AC is rarely used in vehicle electronics, it must be converted to DC. To help with the conversion of AC to DC, full-bridge rectifiers with four diodes are installed within the alternator. The converted DC is then kept in the battery.
When employed in power systems for the house, inverters are also required to convert electricity from batteries into AC power. This is an additional expenditure that can be rather expensive. In addition to this issue, waste is linked to converted energy, which is estimated to be between 5% and 15%. The vast majority of AC-compatible equipment utilizes excessive amounts of electricity.
Alternating Current (AC) is still widely utilized in most applications despite its drawbacks since Direct Current (DC), although having advantages, too has certain drawbacks and one has a feature that the other power type couldn’t provide.
Due to its benefits over direct current in terms of transmission and transformation, alternating current is now mostly employed for electric power distribution. However, it is still true that DC provides benefits for unique applications. When it is not feasible to transmit AC power across great distances, DC electricity is an alternative.
Subsea high voltage DC transmission lines are an example of such an application. Here, electricity generated in AC form is converted to DC at a switching/terminal station and then transmitted via a subsea network of cables before being converted back to AC at another terminal station and delivered to the customers.
The greater expense of installing switching yards and terminal stations, however, is a significant drawback of these high voltage transmissions. The components also have a low capacity for overloading and require expensive maintenance.
It’s challenging to decide which is preferable because both AC and DC have their applications. It would be more accurate to argue that each has advantages.
Where Is DC Employed?
There are several uses for DC power. These consist of:
Batteries, such as the AC converter battery in a vehicle, are charged using a DC battery.
Electronic devices that use direct current frequently use DC volts (for example televisions, radios, computers, and printers). Something that has a constant polarity and never changes direction is referred to as “direct current.” An electronic device is typically powered by a tiny AC; nevertheless, the electrical current inside the device successfully turns the little AC power into direct current power by employing capacitors and diodes to store energy until enough voltage is available to drive a load. Therefore, all direct current electronics gadgets employ dc generators internally even if the input for these devices may be ac output mains voltage from your home’s electrical system.
Fluorescent lighting, like the lights in your office building or store, uses DC batteries. Every fluorescent light fixture has a large ballast at the bottom that contains a bridge rectifier that converts the AC power from an electrical system into direct current flows to charge the large capacitors there. The stored energy is then discharged into the cathodes of all of those tiny gas-filled tubes inside each fluorescent light fixture. Unlike alternating current, which regularly changes direction, DC voltage only travels in one direction from high voltage down through a load (such as an incandescent bulb) to the ground. This is similar to how water runs downhill in pipes.
Nissan Leaf battery by Tennen-Gas / CC BY-SA 3.0. AC is normally produced by the alternator. This output instantaneously transforms to DC for use. Previously, automobiles’ DC generators helped provide energy. However, these DC generators were subsequently replaced with alternators due to a significant increase in the use of vehicle electricity.
The Conclusion
There is plenty to learn about the electronics in your vehicle, but the most crucial thing is to avoid being perplexed. Simply said, all batteries are DC, and automotive batteries are not an exception. It’s also crucial to routinely get the vehicle batteries tested and cleaned.
If you’ve made it this far, you’ve probably concluded that the battery is a crucial component of your car’s electrical system as a whole. Your urgent query, “Is a car battery AC or DC,” has successfully been resolved.
Yes, a car battery serves as a DC power source for all of the DC electrical parts of the vehicle. The alternator, AC converters, and rectifiers are some other parts that cooperate with the battery.
Always check your car battery to make sure it’s free from damage, largely because if such damage is overlooked, it might result in larger and more expensive repairs or replacements.


Jim Wicks is the founder of MotorVehicleHQ. With over two decades of experience in the automotive industry and a degree in Automotive Technology, Jim is a certified car expert who has worked in various roles ranging from a mechanic, car dealership manager, to a racing car driver. He has owned more than 20 cars over the past 15 years. Ask him about any vehicle you see on the road and he can tell you the make, model and year. He loves the aesthetics of all things cars, and keeps his vehicles in pristine condition.
In his free time, Jim enjoys getting his hands dirty under the hood of a classic car or taking long drives along the country roads. His favorite car? A 1967 Shelby GT500, a true classic that, according to Jim, “represents the pure essence of American muscle.”