If you’re looking for information on how to solve the P0172 error code, know that it means your engine bank 1 is using too much fuel. An excessive amount of fuel may be caused by an abundance of fuel or a scarcity of air.
Whatever the cause, all you need to do is utilize an OBDII scanner to validate the problem, and then either clean the MAF sensor or replace the oxygen sensor, depending on the situation. If neither of these two approaches solves your issue, you must take it to the closest repair shop.
Even if warning lights are related to minor problems, they are still quite serious. Ignoring these lights won’t make things worse or have undesired effects. So, the advice of automobile specialists is never to disregard a warning signal.
You should be aware of some of the typical warning lights and error codes in your car as a driver. For instance, the P0172 error number is significant since it has to do with the air-fuel ratio in your engine.
Everything you want to comprehend the P0172 code and be aware of its typical causes and symptoms is covered in this article. We also give you a ballpark figure of how much it will cost you to have the issue fixed professionally or at home.
Error Code P0172: What Does It Mean?
The airflow and fuel injection systems’ system components are continuously monitored, communicated with, and controlled by the vehicle’s computer, also known as the brain of the vehicle.
For instance, the car computer will display P0172 if it determines that the exhaust fumes leaving the tailpipe include either too much gasoline or insufficient air.
A check engine light or malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) by Wikiuser100000 / CC BY-SA 3.0. Every time the P0172 error code appears, the car’s computer receives a signal from the engine’s computer, which activates the check engine light. There could be several different causes for the check engine light to illuminate; it doesn’t necessarily mean that the air-fuel mixture is the only problem.
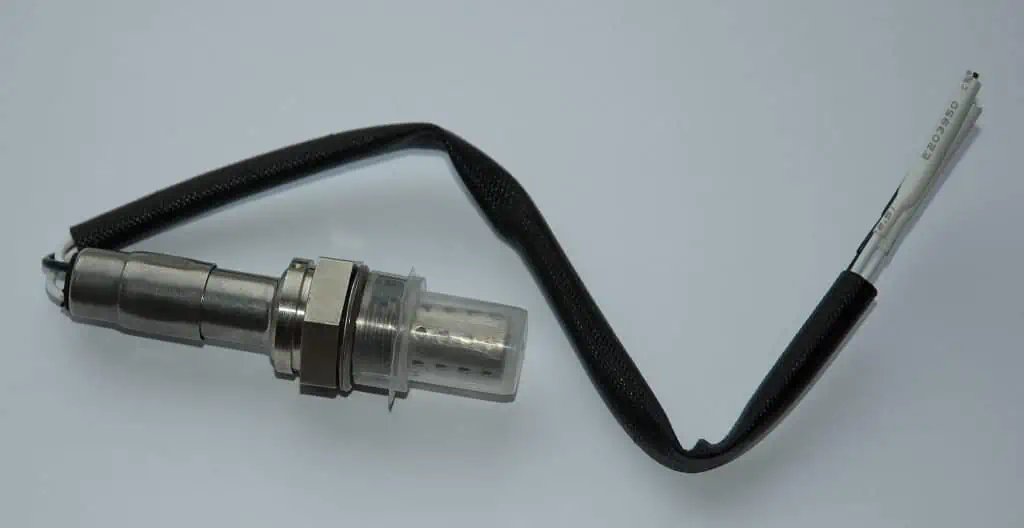
The air-fuel mixture ratio in the engine is monitored by the automobile computer using readings from several devices, including the mass airflow (MAF), oxygen sensors, and manifold absolute pressure (MAP).
The most common method used by oxygen sensors to gauge the engine’s air-fuel ratio is to count how much oxygen and carbon monoxide are in the exhaust gases as they leave the tailpipe. In motor vehicles, an ideal air-fuel ratio is 14.7:1. Because studies have shown that it provides the best power production and low fuel usage, manufacturers favor this ratio.
It’s crucial to understand that the automobile computer is not a phony that simply gathers data from various sensors and displays it for the driver. Instead, it gathers these facts and uses them as needed.
For instance, the computer in your Honda can slightly alter the ratio of air to gasoline. However, if the ratio offset is excessive, the Honda will display P0172. Of course, all internal combustion engines follow the same rules.
Rich refers to an air-fuel ratio that is either too high or too low. Anyhow, if your powertrain control module displays P0171, the car’s computer has determined that there is either insufficient gasoline or too much air in the system.
The mixture of Air to Fuel and Its Relation to Code P0172
Any vehicle’s combustion system has to receive a precise volume of air to fuel per a ratio defined in the owner’s handbook. Any change in this ratio has the potential to impact engine performance as a whole.
For instance, a car is said to be overly rich if it receives more fuel than is required for the engine. On the other hand, you are dealing with poor fuel when the engine does not have enough fuel or receives too much air.
Your car’s overall performance will be impacted in either scenario. Some of them may interfere with the car’s overall fuel efficiency, while others may have a minimal impact on the car’s drivability and engine performance.
The check engine light turns on whenever this occurs because the engine’s computer sends a signal to the car’s computer. When the check engine light comes on, it doesn’t necessarily imply that the air-fuel mixture is the sole issue; there may be several other explanations.
We’ll teach you how to determine whether or not a P0172 code issue is the cause of the check engine light in the sections that follow.
Why Does Error Code P0172 Occur?
The Ford or your particular automobile model’s car computer may throw the P0172 error due to several factors. However, blocked or unclean mass air flow sensors and subpar oxygen sensors are the most frequent causes. further likely reasons include;
A three wire oxygen or lambda sensor by Mnemo / CC BY-SA 3.0. By counting the amount of oxygen and carbon monoxide in the exhaust gases as they leave the tailpipe, oxygen sensors can determine the engine’s air-fuel ratio most frequently. An optimal air-fuel ratio for motor vehicles is 14.7:1. Manufacturers like this ratio because tests have proven that it produces the most power while using the least fuel.
- Leak in the vacuum system
- The fuel pressure regulator is broken
- The thermostat is stuck on “open.”
- Throttle body position sensor malfunction
- MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor defect
- Unreliable fuel injectors that leak gasoline into the cylinders
- Defective or constrained gasoline lines
- Faulty spark plugs
- Dirty or clogged air filter
- Ineffective powertrain control module (not likely the case, though, possible)
What Symptoms Represent Error Code P0172?
Similar to other system problems, a P0172 will show a few problems that show your engine is running rich. The check engine light will first appear on the dashboard thanks to the powertrain control module. The signs that an automobile is running rich are listed below.
If your car’s engine is running on a rich fuel mixture, it will use more fuel. The driver may not notice any symptoms other than an illuminated Check Engine Light because of the complex procedures the PCM/ECM must follow to ensure the fuel system is balanced. Extreme situations when one or more components have failed can cause symptoms that are mild to engine-damaging.
Unburned fuel in the exhaust lines could catch fire and harm parts like the catalytic converter, making the exhaust system another weak point. Keep an eye out for these signs to be informed in advance about these issues:
1. The Check Engine Light Illuminates
Every time a system unit in your car experiences a fault, the check engine light comes on. No exception applies to the P0172 on Mercedes and other automobiles. The check engine light’s purpose is to alert the driver about impending systemic problems.
2. Poor Fuel Efficiency
The P0172 code indicates that the combustion chamber is receiving too much fuel. Therefore, a high rate of gasoline consumption is one of the obvious signs. This entails frequent trips to the gas station and additional spending.
A typical car engine by Yones / CC BY-SA 3.0. Your car’s engine will consume more fuel if the fuel mixture is rich. Due to the intricate processes the PCM/ECM must carry out to guarantee the fuel system is balanced, the driver may not experience any symptoms other than an illuminated Check Engine Light. Extreme circumstances where one or more components fail can result in symptoms ranging from minor engine damage to severe ones.
3. Erratic Idling
Engines are built by automakers to accept a balanced ratio of air-fuel mixtures. Therefore, you will have rough idling if there is a big amount of air or fuel.
4. Engine Stutter
Engine reluctance is another sign of P0172 problems, especially when towing, going uphill, or driving on a flat road. The engine could appear to be hesitant to you.
5. Misfiring Engine
When driving, a P0171 on a VW will result in engine misfiring, hesitation, and stuttering. The extra ratio will determine the misfire and the hesitation.
6. Insufficient Engine Power
The performance of the engine as a whole will be impacted if the air-fuel ratio has been affected. Consequently, depending on how serious the P0172 code is, you may notice an engine power loss.
NOTE: Take into account that all of the symptoms indicated might be caused by several other problems. As a result, you cannot assume that the presence of a check engine light indicates that a P0172 code is the cause of your issue. Similar to the P0172 code, engine misfiring isn’t usually a sign of a problem.
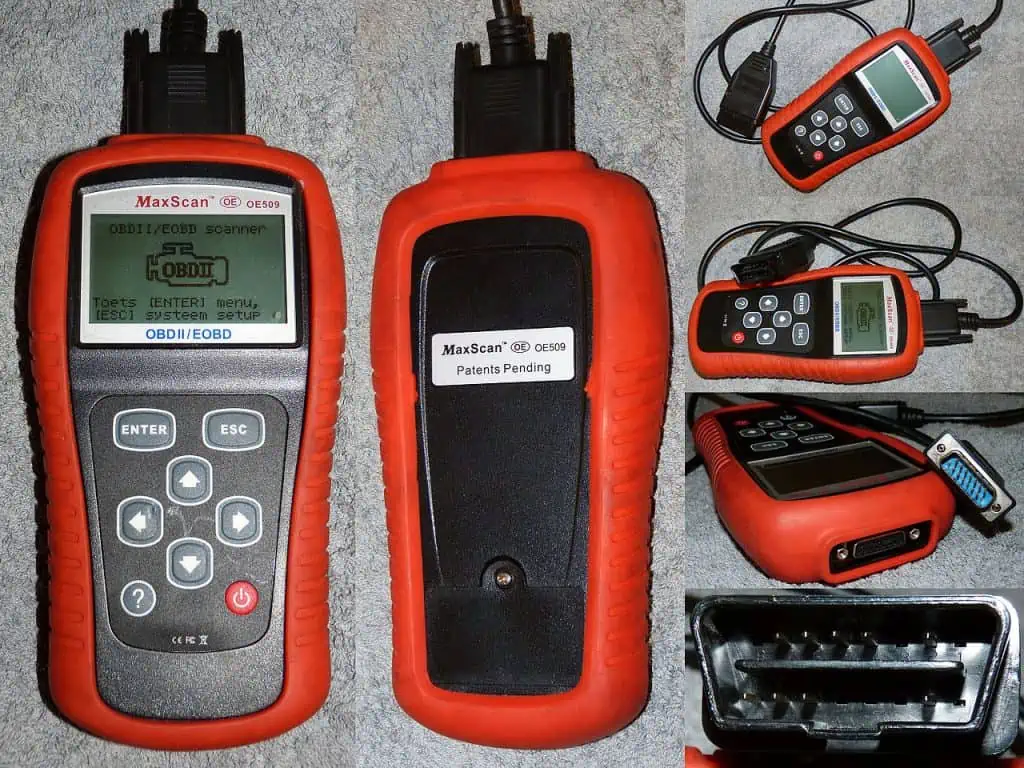
You must thus confirm the issue before attempting to fix the P0172 code, and the quickest and most precise method to do this is by using an OBDII scanner.
Is Error Code P0172 Serious?
The P0172 diagnostic issue code has a moderate level of severity. It won’t deter you from driving. However, due to the engine warning light being projected, the car will fail the state emission check. Second, an engine will emit black smoke from the tailpipe if the fuel mixture is too rich. This harms the environment.
A P0172 Error Code: How Can I Diagnose It?
The air/fuel mixture was not automatically regulated by the car’s computer when error codes P0172 and P0175 appeared on your dashboard. Bank 1 is covered by Code P0172, whilst Bank 2 is covered by the other code.
In the case of P0175, it primarily applies to V6 and V8 engines because four-cylinder engines typically have a single bank. There are a few exceptions, though, including powerful six-cylinder engines.
When the issue code indicates that the fuel system is overly rich, the computer is likely siphoning in extra fuel, which, if it goes on for too long, is known as long-term fuel trim. The optimal range is between 1% and 2%. When the code P0172 appears, it indicates that the fuel trim is around -15% (but it may potentially be -30%).
Mass Air Flow sensor in a 2006 to 2015 automotive diesel engine by Antonín Ryska / CC BY-SA 4.0. The MAF sensor could be to blame for the P0172 error code. The sensor must be located, and it is frequently between the air filter and the throttle body. For further instructions, refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you need help identifying the MAF sensor.
When this occurs, the engine’s computer notifies you that the fuel system or oxygen sensor is malfunctioning.
You must inspect the scanner and search for the least of the three ranges for long-term fuel trim to identify P0175 and P0172. Look at the idle reading as well. The absolute minimum is 3,000 RPM with no load, and 3,000 RPM with 50% load.
After that, note the code’s free frames and identify the range or ranges that failed. Identify the circumstances under which the failure occurred.
Step 1: Use a Scan Tool to Inspect the Car
Plug your scan tool into the OBD port that you can find on the car. After that, scan the car to make sure no other codes are present. Before moving on to the next stage, repair any additional codes that the scanner produces.
Step 2: Check the Vacuum Hoses
Check the vacuum hoses to make sure there are no leaks in any of the lines or hoses. You will hear a hissing sound near the vacuum lines if there is a vacuum leak. It will be challenging for a novice to discern the hissing sound when the engine is operating. Having stated that, you must focus intently and put all other activities on hold.
Step 3: Examine the MAF Sensor and Exhaust System
The P0172 error code may have been caused by the MAF sensor. You must therefore find the sensor, which is often situated between the air filter and the throttle body. If you’re having trouble locating the MAF sensor, you can always turn to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for precise instructions.
Carefully remove the MAF sensor, then use a MAF sensor cleaner to clear out any obstructions or debris that may have become lodged there. It is crucial to clean the sensor since if you hold it horizontally, the spray will fall to the ground and harm it.
Reinstalling the MAF sensor is possible once it has dried completely. Try to check if the P0172 code is still present by testing your car. You must utilize the OBDII scanner to check for any acts of error because the air will still be present even if it isn’t operational, so keep in mind that the code won’t be removed on its own.
Step 4: Examine the Fuel Pressure
Check the fuel systems, paying close attention to the injectors. Unnecessary fuel will be injected into the combustion chamber by a leaking injector. Check each injector individually to make sure they all have the same pressure. Replace any injectors that are pouring too much fuel.
Step 5: Examine the Spark Plugs and O2 Sensors
The oxygen sensor is the second thing you should examine if you receive a P0172 error code. It often sits nearby the exhaust manifold. The owner’s manual for your car should contain a thorough description of where it should be if you’re still having trouble finding it.
An onboard automotive diagnostics handheld scanner (OBD II) by Arp. Once it has fully dried, the MAF sensor can be reinstalled. Test your car to see if the P0172 error code is still present. The air will still be present even if it isn’t working, so keep in mind that the code won’t be deleted on its own. You must use the OBDII scanner to check for any acts of error.
If you need help locating the oxygen sensor in your car, you can also check photographs online or watch videos on YouTube.
When you first started looking for the oxygen sensor, you disconnected it from the catalytic converter and contacted your manufacturer to order a replacement. Install the new sensor, then test your figure. Check the vehicle’s errors to determine if the P0172 code is still present.
Which are the P0172 Common Diagnosis Errors?
The most frequent diagnostic error committed by technicians is failing to inspect the temperature sensor and other cooling system parts. For instance, a car’s engine requires more fuel to warm up to the working temperature while it is cold.
As a result, the powertrain control module may presume the engine is cold and deliver additional fuel to warm it up to the normal operating temperature if the coolant temperature sensor sends a misleading signal to the PCM. Nevertheless, before replacing any parts, it is crucial to make sure the temperature sensor is in good working order.
What is the Procedure for Fixing the P0172 Code?
Fortunately, there are many ways to fix code P0172, but the most effective one will depend on the precise cause. Even though you might only need to clean it, replacements are frequently necessary.
As a result, there isn’t a single answer to this issue. As was indicated above, you must first accurately diagnose the code before making any required repairs.
Of course, keep in mind that every vehicle is different. You should glance over the factory repair information for your specific application when diagnosing and correcting OBD-II error codes. For various causes, various remedies are needed. Here are a handful of the most typical answers to this issue:
- Check the PCV vacuums and hoses for damage, and replace any essential parts.
- Make the MAF sensor clean. To be certain of where the MAF sensor is, check your owner’s manual. It is preferable to remove this sensor before cleaning it with an electronic cleaner or brake cleaner. However, take care to avoid damaging it. Before reinstalling the component, make sure to properly dry it.
- Look for leaks, cracks, and pinches in the fuel lines.
- Examine the fuel pressure.
- Examine the fuel injectors for debris. Use fuel injector cleaner to clean them yourself, or have them professionally cleaned or changed.
- Look into the exhaust leak around the first O2 sensor. Even if it’s doubtful, this might still be the root of the issue.
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device by The RedBurn / CC BY-SA 3.0. Putting off and delaying the repairs could seriously ruin the catalytic converter, one of the most expensive parts of your car, even though you will still be able to drive it for short distances. If you can manage the catalytic converter repairs, it shouldn’t matter why you can’t fix the P0172 problem code.
Fixing the P0172 Code: How Much Does It Cost?
Of course, the major factor that led to the P0172 code will have a significant impact on the response to this inquiry. In most cases, the issue is caused by a problem with the oxygen sensor, which is a simple problem. Normally, you shouldn’t have to pay more than $60.00 to replace the sensor.
If the issue was ignored for a longer period, you might introduce them into the catalytic converter, which in more recent automobiles might cost you easily up to $3000 or even more.
We always advise fixing the issue yourself or by going to a qualified mechanic anytime you observe symptoms of a P0172 code.
Remember that the labor expenses involved in correcting a P0172 error code might vary greatly depending on whether you visit a dealership or a small repair shop.
Modern car owners occasionally choose to go to the dealership even if it will cost them more since they will feel more assured that highly skilled and knowledgeable specialists will be working on addressing their issues.
As a result, there is very little danger of seriously harming the catalytic converter or any of the components nearby.
Can the P0172 Code Clear on Its Own?
Sadly, unlike other error codes, the P0172 code will not disappear after the issue is resolved. As a result, you must attach an OBDII scanner to the vehicle.
Ask the scanner to rescan the automobile after you’ve linked to it. P0172 should appear as an inactive error. You can go ahead and request that the tool remove this error so that you can do away with it forever.
Request a scan of the vehicle once again to make sure there are no more problems or to verify that the P0172 code issue has been resolved.
Is It Safe to Drive a Car That Shows Symptoms of the P0172 Code?
Unfortunately, you won’t be able to travel far in your car when the P0172 code is activated.
Even while you will still be able to drive the car for short distances, putting off and postponing the repairs could cause serious harm to the catalytic converter, one of the most expensive components of your vehicle.
It shouldn’t matter why you can’t fix the P0172 error number as long as you can handle the catalytic converter repairs. Did you know that certain automobile replacement costs for Catholic converters can reach $3000 or higher? Who desires to handle that?
An electronic control unit (ECU) or an electronic control module (ECM) by Specious / CC BY-SA 3.0. Your car will use more fuel if the fuel mixture in the engine is rich. Due to the intricate procedures the PCM/ECM must follow to ensure the fuel system is balanced, the driver may not experience any symptoms other than an illuminated Check Engine Light. Symptoms that range from moderate to engine-damaging can occur in extreme instances where one or more components have failed.
Therefore, if none of the DIY fixes suggested in this article worked for you, you must take your car to a qualified repair as soon as you notice any of the P0172 code’s symptoms.
The Conclusion
By this point, you have seen the issue’s significance, causes, symptoms, diagnostic blunders, and the ideal way to identify and resolve it. You can identify and fix the problems on your own. Furthermore, it can be difficult to identify and address the problem because several difficulties can result in the auto computer logging P0172.
So it’s best to start with the simplest and least expensive solutions. First, inspect the mass air flow sensor and see if the air filter is clogged. After that, proceed to the expensive and improbable causes.
The P0172 error number means that one side of your engine’s bank has more fuel than air. For your car to run efficiently, the air-fuel mixture ratio must be correct.
It is crucial for you as a driver to address the P0172 quotation right away to avoid dealing with significant repair expenses that might cost you up to $3000, if not more if the catalytic converter needs to be replaced.
You learned everything you needed to know about the P0172 error code in this article, including its primary causes, symptoms, recommended fixes, and projected repair costs.

A check engine light or malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) by Wikiuser100000 / CC BY-SA 3.0

Jim Wicks is the founder of MotorVehicleHQ. With over two decades of experience in the automotive industry and a degree in Automotive Technology, Jim is a certified car expert who has worked in various roles ranging from a mechanic, car dealership manager, to a racing car driver. He has owned more than 20 cars over the past 15 years. Ask him about any vehicle you see on the road and he can tell you the make, model and year. He loves the aesthetics of all things cars, and keeps his vehicles in pristine condition.
In his free time, Jim enjoys getting his hands dirty under the hood of a classic car or taking long drives along the country roads. His favorite car? A 1967 Shelby GT500, a true classic that, according to Jim, “represents the pure essence of American muscle.”