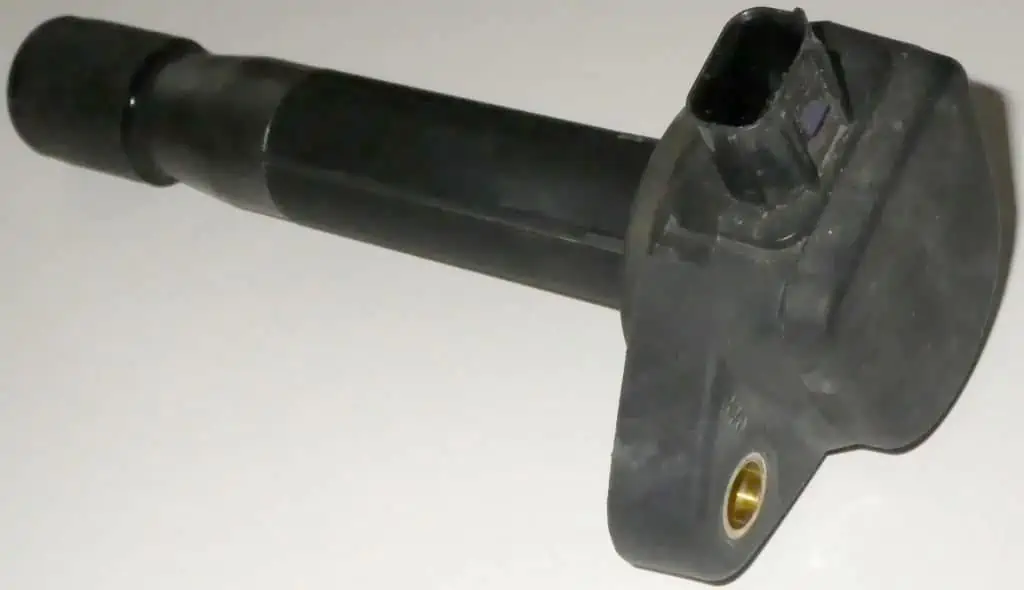
The metal components known as ignition coils are in charge of controlling an automobile’s ignition electronically. As a result, damaged ignition coils can cause serious mechanical and performance issues with your automobile.
Having trouble starting the automobile, having the engine stall, and losing power while driving is the main signs of a faulty ignition coil.
These signs are readily mistaken for several different engine issues. As a result, we must understand how to identify a damaged ignition coil.
At first, you realized you had a distributor issue when your car’s engine misfired and the “check engine” light came on. Nowadays, most new automobiles include coil packs in place of distributors, which improves the efficiency of electronic transmissions.
Nevertheless, since a coil pack ignition system has fewer moving parts, it might be difficult for a car owner to diagnose and fix ignition coil issues.
The heat that the ignition coils are subjected to is known to cause failure. Here’s how to identify damaged ignition coils.
A transformer called an ignition coil is used to change the current going to the spark plug so that it can spark as well as start the engine. It is a crucial part of the ignition system for cars, and if it is broken, your automobile won’t start.
As a result, if this component malfunctions, your car’s engine might experience major issues.
In this piece, we’ll look at the signs of a failing ignition coil and consider what precautions may be done to prolong the ignition coil’s lifespan. Let’s first quickly review the warning indicators to watch out for:
The most typical sign of a faulty ignition coil is a misfiring engine and a dashboard check engine light. Additionally, you can notice symptoms like an engine that stalls, higher fuel usage, and engine sounds.
Because the ignition coil is such a crucial component of the automobile engine, a damaged ignition coil can cause a variety of symptoms.
The Ignition Coil: What Is It?
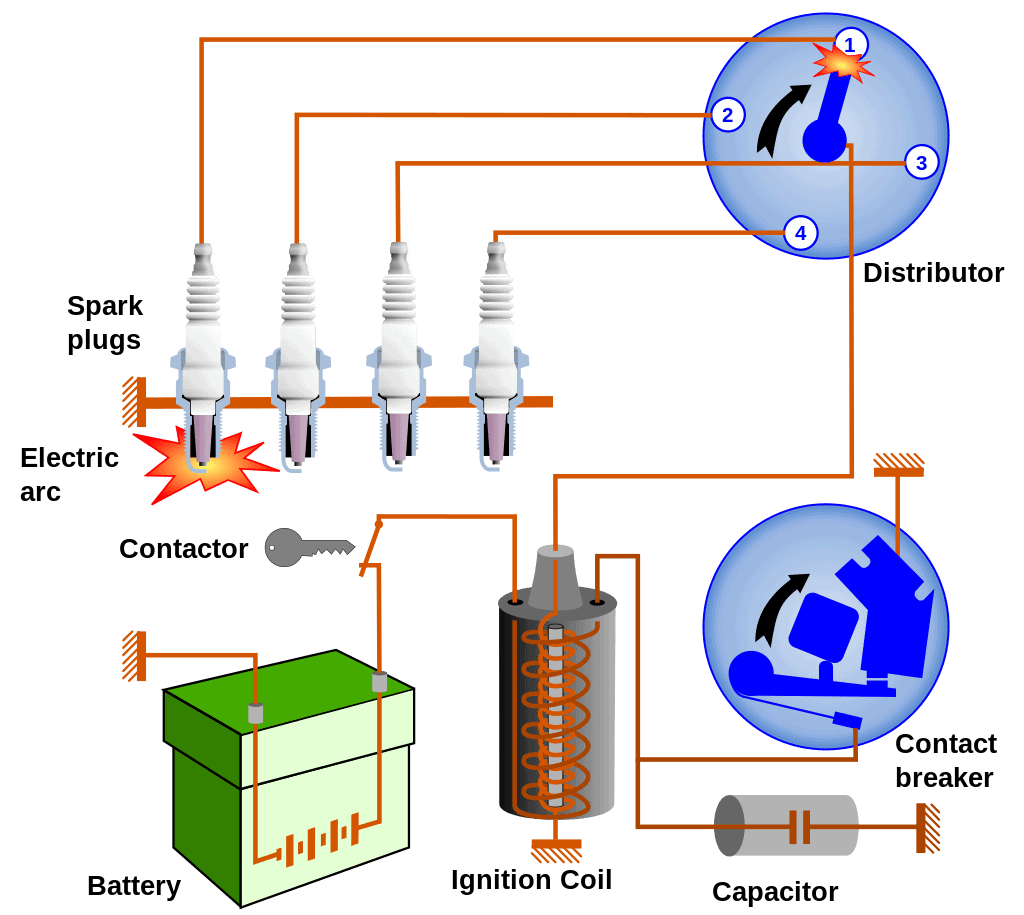
Combustion is necessary for an engine to start and run continuously. Air, fuel, and spark are the three essential ingredients for combustion. The spark is produced by the spark plugs, but they need an electrical current to do it.
Dual ignition coils by Liftarn / CC BY-SA 3.0. Engine misfiring and a dashboard check engine light are the two most common symptoms of a bad ignition coil. Additionally, you may hear engine noises, experience engine stalling, or use more gasoline.
Thousands of volts of energy are required for a spark plug to ignite. Car batteries are typically just 12 volts, which is significantly below the voltage required for a spark plug to ignite.
Electrical transformers are exactly what ignition coils are. The ignition coils absorb the battery’s power and increase it from 12 volts to the tens of thousands of volts the spark plugs need to operate effectively.
Where Is the Ignition Coil Located In a Car?
When the engine has separate ignition coils, they are often found on the engine’s head, on top of the spark plugs.
However, if you just have one ignition coil and one distributor, the distributor is often mounted close to the ignition coil on the car’s body.
What Function Does an Ignition Coil Serve?
A car’s ignition coil is just a transformer that increases a car battery’s meager voltage to a level strong enough to ignite the gasoline and start the engine.
Ignition coils are specifically electrical devices made up of two wire coils wound around a metal core. The secondary coil of an automobile ignition coil contains many more spins than the primary coil because it functions as a step-up transformer.
The secondary coil continually interrupts the electric current as it travels from the battery to the main coil, producing a powerful magnetic field that raises the voltage of the secondary coil over the original 12 Volts from the vehicle battery.
In contrast to the old approach, which required the use of a distributor for power transmission, the coils then fire the sparkplugs directly in response to an instruction from the engine computer.
The engine control unit of the automobile is now informed by ignition modules and car sensors when to open or close the coil current. To keep track of the order of spark plugs, modern automobiles also incorporate timing lights.
A coil of wire that serves as a conductor is found within a spark plug. To move electrical currents through the wire coil, a circuit switch on the coil opens and shuts.
The coil’s windings conduct current when the switch is open. The coil is surrounded by a magnetic field as a result, increasing the voltage of the electrical current. When the switch is turned off, the magnetic field returns to the coil and may then be sent to the spark plug.
Nowadays, the majority of ignition coils feature a two-coil wiring arrangement. A magnetic field produced by the first coil can have a 10x to 20x increase in voltage compared to the initial 12 volts.
Since the second coil wire is smaller and hence generates more voltage through the magnetic field, the voltage may be increased by 100 times, exceeding 20,000 volts.
Which Ones are the Most Common Bad Ignition Coil Symptoms In a Car?
As previously mentioned, ignition coils manage one of a car’s fundamental functions. To make an early adjustment, drivers should be aware of the reasons for ignition coil failure as well as the signs of coil dysfunction. Some of the warning signals that the ignition coil is ready to fail are listed below.
Bosch ignition coil by Sonett72. Two wire coils twisted around a metal core make up the specialized electrical device known as an ignition coil.
1. Reduced Power Output
Cars run poorly because defective ignition coils produce less power. At idling, the automobile breathes roughly and moves forward slowly. These early indications should serve as a reminder to fix your vehicle to prevent more damage and costs.
The vehicle’s power output has decreased as a result of inefficient fuel combustion caused by erratic sparks. Fewer revolutions per minute as a result of low power production are evident in the car’s slow acceleration and subpar engine performance.
2. Having Trouble Starting the Engine
Powerful sparking is necessary for an engine to turn over. While you may assume that the spark plugs are responsible for this, your car’s very own small transformer is really what generates the thousands of volts that are supplied to the electrodes.
To ignite the fuel mixture, the spark plugs need a powerful current, which the ignition coil helps to deliver. The spark plugs might not be able to jump the gap if the ignition coils can’t provide enough energy.
It is extremely uncommon for more than one ignition coil to malfunction at once, but if two or more do not function properly, a no-start problem may occur.
3. Engine Misfires When the Car Travels at Fast Speed
In other cases, a single-coil failure might not have any noticeable effects on how well your car performs.
Other times, though, you can hear a few minor misfires here and there. A single ignition coil frequently fails without any prior notice. However, that does not imply that you should disregard the infrequent failures.
Misfires that happen beyond a specific speed limit may be a sign that one of your ignition coils needs to be replaced. The failure of one of them may also portend the oncoming failure of the other since worn-out spark plugs or shorted wire are the two main causes of ignition coil failure.
Swapping the ignition coil is one quick technique to check for a damaged ignition coil if you have an OBD II scanner. A faulty ignition coil is more likely to cause the scanner to detect a misfire in only one cylinder.
You may change the defective ignition coil out for a good one to determine if the ignition coil is really what’s causing the misfire. If the scanning tool shows a misfire in the other cylinder this time, you’ll know what’s going on.
4. The Car Experiences a Rusty Idle
Misfires at idle may occur if the casing for your ignition coil pack has been damaged. The coil may not be able to deliver electrical charge straight to the plugs when it is damaged or burned, therefore it will instead try to locate the quickest path for the charge to depart.
Therefore, the current could attempt to avoid the electrode and make its way down the shortest path, which would be the sidewalls of the cylinder head, rather than passing through the spark plugs and into the engine. This is a certain method for ignition coils to malfunction.
If the ignition coil housing looks to be damaged in any way, it may be an obvious clue that your ignition coils are to blame. You might try to closely inspect the ignition coil housing.
Aceon Bright Ignition Coil by Aceonhost / CC BY-SA 4.0. If the ignition coil pack’s casing is destroyed, misfires might happen while the engine is running. When the coil is broken or burnt, it might not be able to send electrical charge directly to the plugs.
5. Lower Gas Mileage
The ignition can sometimes stop working on its own and other times it can stop working gradually. Although an ignition coil that is progressively degrading appears to be functioning correctly, it hurts your fuel efficiency.
When you fill-up your automobile, you may check your mileage to see whether that is the case. You can have a defective ignition coil if your mileage keeps dropping.
As a result of the vehicle injecting more gasoline to make up for the ignition coils’ poor energy output, the mileage gradually declines. When you have a defective ignition coil, your mileage also suffers since extra fuel is injected because the oxygen sensor can’t acquire accurate readings.
Poor gas economy results from inappropriate fuel combination combustion. Although the decrease in fuel economy may not be very noticeable in the case of an ignition coil failure.
This often happens when only one engine cylinder performs incorrect combustion. Additionally, even though it’s unusual if two or more ignition coils fail, your fuel efficiency might drastically decline.
6. The Check Engine Light on Your Car’s Dash Illuminates
Your check engine light may quickly turn on if there are frequent misfires and restricted system operation. Your vehicle’s internal diagnostics can assist you in identifying problems before they have a chance to become more serious.
The possible error code for a faulty ignition coil is P0351, which denotes a primary/secondary circuit problem.
You might try adding new ignition coils to try to solve the problem. It is a really simple process that doesn’t call for a lot of tools. Although it might not be able to identify the root cause of the coils’ initial failure.
7. Oil Spillages from the Car
One of the hot ignition coil issues is oil leakage. Because they can’t adequately transfer the energy from the battery to the sparkplugs, defective ignition coils overheat. Engine pipe cracks brought on by overheating result in oil leaks.
Bad Ignition Coil Symptoms
Under normal driving circumstances, ignition coils are vulnerable to wear and tear and eventually fail; this often occurs around the 100,000-mile mark.
Many factors, such as overheating, vibration, moisture infiltration, engine oil leaks, or problems with other ignition system parts, such as faulty spark plugs, can cause an ignition coil to generate more voltage than usual, drastically diminishing the coil’s useful life.
1. A Spark Plug Well Oil Leak
An oil leak in the spark plug tube can prevent the ignition coil from functioning properly, lead to engine misfires, and potentially harm the coil. This often occurs as a result of a breach in the valve cover’s spark plug tube seal. The leak is largely stopped by replacing these seals.
2. Damage from Rats, Worn Out Connectors, or Wiring Harness
There is a good chance that a rodent has let up some steam in your car’s engine compartment if bite marks are seen underneath the hood.
Ignition coil module by Cschirp / CC BY-SA 3.0 de. The spark plug’s current is changed by a transformer known as an ignition coil so that it can spark and start the engine. Your car won’t start if it is damaged since it is an essential component of the ignition system.
Then, it’s crucial to thoroughly inspect all the cables, hoses, electrical wires, and connectors for the ignition coils for damage.
You may get an error code between P0350 and P0362 when you attach a code scanner tool, which denotes an ignition coil circuit malfunction when the electrical wires or the connector for the ignition coil become faulty.
3. A Faulty Fuse
Electricity is required to operate the ignition coils. Faulty fuses cause the circuit to be stopped, which prevents the coils from firing.
To determine the precise placement of the fuse for the coils in your car, see the owner’s handbook or the fuse box lid. Replace the blown fuse with a fresh one that has the required amp rating.
Use a fuse puller or needle nose pliers to remove the fuse from the fuse box, then hold it up to the light to see whether it is working. The fuse has blown if the metal strip is torn in half in the middle.
You must swap it out for one with the same amps and, thus, the same color. It makes no difference which way you enter the fuse.
How Do You Diagnose Bad Ignition Coil Symptoms
Examining the coils themselves should be the first and most important inspection. They are probably damaged if they have fractures, burn marks, are melted, or are covered with oil. Try these methods for evaluating ignition coils if the coils appear to be in good condition upon visual inspection:
1. Alternating the Coils
Swapping the ignition coils is the quickest way to determine if the problems you’re having are caused by the spark plugs or the ignition coil.
Swap the ignition coils for cylinders 2 and 1 if you, for instance, receive an engine code for a cylinder 2 misfire. Once you experience another misfire, clear the engine codes once more and continue driving the vehicle.
The ignition coil is damaged if the misfire code now indicates cylinder 1. The spark plug may be faulty (or there may be another problem) if you follow this procedure and the engine code still indicates that cylinder 2 is defective.
You may perform the same procedure for vehicles that employ spark plug wires by switching the wires instead. Just be careful not to replace the ignition coil with it; otherwise, you won’t know if the problem is with the wire or the coil.
2. Use of a Multimeter to Test the Coils
If changing coils is not a possibility, the next easiest solution is to test the ignition coil’s coil wires for Ohms resistance.
A multimeter may be purchased, and the positive and negative leads should be connected to the appropriate coil wire terminals. You must measure the ohm readings of the primary and secondary windings.
Depending on how it was made, each ignition coil will have unique contact locations. For the correct coil contact points and appropriate Ohm ranges for each coil winding, consult your owner’s handbook or Haynes service manual.
This approach may produce inaccurate results because ignition coils behave differently with and without load.
Magneto ignition coil by Ulfbastel. Important electromagnetic components called ignition coils raise an automobile battery’s 12V to approximately 100000V. With 100000V, the engine’s cylinders may be ignited and spark-ignited, which is enough to allow fuel combustion and let the car move.
3. Alternative Tests
Your best bets are the two alternatives listed above. Although approach #1 is our preference, it can be a headache if you also have spark plug wires and need to perform many swaps to identify the issue.
There are more costly, more recent coil-on-plug testers that enable you to test coils without removing them from the car, as well as more modern ignition coil testers and inline spark testers.
Testing an ignition coil may be risky and delicate. When you suspect an issue with your ignition coil, carefully follow these more complex measures.
- Before opening the hood if your car was running, be sure it has had enough time to cool. For the next stages, it would be helpful if you had your toolbox with you.
- To prevent electrocution, take the battery’s negative connection off after opening the hood. If vision is poor, locate the terminal using your underhood work light.
- Locate your ignition coils on the engine then unscrew the nuts holding them.
- Verify the main as well as the secondary winding voltages advised in the owner’s handbook of your automobile.
- Connect the positive as well as negative terminals of the multimeter to the corresponding terminals on the thicker primary winding to test it first.
- Verify that the multimeter readings match the suggested readings in your handbook.
- A value that is larger than what is advised signifies that the coil was open, whereas a reading of zero implies that the coil short-circuited.
- Connecting comparable connections to the multimeter will now allow you to test the secondary winding of the ignition circuit similarly. To determine whether they broke down, compare the readings you obtain to those listed in your handbook.
- If your automobile has numerous ignition coils, the only method to determine which ignition coil is defective is to test them all.
Spark plugs are typically to blame for ignition coil problems, however, they may also show excellent readings despite physical damage and reduced insulation. Therefore, examine the other components first to determine what is causing the ignition coils to continually fail before rushing to replace them.
Find out from your user handbook the recommended spark plug resistance ratings, then test them with an ohmmeter to see if their values match the compliance ranges. Make sure the spark plug wires are in order and are accurate as well.
How Can You Replace a Bad Ignition Coil in Your Car?
Your automobile will suffer harm if it is driven with a faulty ignition coil. To swap out your broken coil for a new one, follow these procedures.
1. Put Your Safety First
Before opening the hood, make sure your automobile is cool. Before you do anything else, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery, assuming you have read and comprehended the user handbook for your car.
Please be aware that if you want to leave your automobile disassembled for a long period, certain vehicles advise using memory retention.
Car ignition system by Frédéric MICHEL and PiRK / CC BY-SA 3.0. An ignition coil may create higher voltage than typical due to a variety of circumstances, including overheating, vibration, moisture penetration, engine oil leaks, or issues with other ignition system components, such as malfunctioning spark plugs. This may significantly reduce the coil’s usable life.
2. Take Away the Coils
The most challenging aspect of taking ignition coils out is getting around barriers like the spark plug and coil insulator boots.
You need a new gasket if your vehicle requires the removal of the plenum manifold to access the ignition coils.
Remove the ignition coil bolts with caution so as not to harm the plastic electrical connector. To slip and remove the insulator boot from the spark plug, gently twist it.
Carefully carry out each of these steps since the next time you start the automobile, a misfire will result if the insulator boot tears and a piece ends up at the spark plug. To avoid confusion during the evaluation, remove each coil one at a time and label each one with a picture, a number, or a coil pigtail.
Before changing the ignition coils, thoroughly inspect each coil insulator boot for any indication of oil or other contaminants and rectify any leaks.
3. Examine Each Ignition Coil
Because occasionally when the check engine light flashes, it simply indicates a misfire, you need to examine the ignition coils. The ignition coils may not have been the only item to blame for the misfire. Find an auto shop or a code reader to determine what the code meant.
The code will link the misfire to the problematic cylinder, and from there, you may determine which ignition-related component was to blame.
Whether you have removed several coils and have determined that the ignition coil side causing the misfire is on one side, consider switching the coils to see if the problem spreads to the other side. You can go on to step number 4 if it does. That is another method for determining whether the ignition coil is damaged.
Use a multimeter to test both coils as previously described to find the problems if the misfire doesn’t follow the coil.
4. Set Up the Replacement Coils
Before installing your new ignition coils, lubricate them. Verify that the oil is the appropriate one. Check the pigtail connections and terminal pins once again.
To provide a barrier against moisture, apply dielectric grease to the insulator boot of the new ignition coil. The next time you need to remove the coil, the grease will also help to decrease friction.
Push the coil toward the spark plug with caution, secure it with the bolt, and then reattach the electric pigtail to complete the process.
Returning the removed parts now allows you to evaluate whether the ignition coil repair was effective by driving your vehicle.
How Much Does the Bad Ignition Coil Replacement Cost for a Car?
Depending on the automobile type and labor expenses, the typical cost to replace a single ignition coil ranges from $60 to $350. An ignition coil might cost anything from $30 to $150. An ignition coil requires work that ranges from $30 to $200.
In many circumstances, replacing an ignition coil is rather simple and you can do it yourself. However, depending on the automobile model, the process might take an hour or more, so in certain cases, you can expect to pay quite a high replacement cost.
Plug top coil from Honda by Halpaugh / CC BY-SA 3.0. Every coil insulator boot should be carefully inspected for any signs of oil or other pollutants before changing your ignition coils, and any leaks should be fixed.
Although changing the ignition coil is frequently simple, if you don’t feel confident doing it yourself, take your car to a professional and let them do it.
How Often Should Ignition Coils Replacement Be Done?
Ignition coils do not have a service interval as spark plugs do. They often endure for a long time before turning bad and typically reach the end of their useful lives independently. Therefore, you may replace it if you locate one that has degraded or otherwise has a lower capability.
The failure of one ignition coil does not always portend the failure of the others, at least not soon. Intriguingly, it has been shown that replacing spark plugs on schedule can assist ignition coils last longer.
Therefore, aim to change the spark plugs before they are significantly worn out if you want to be on the ball with your ignition coil maintenance.
How Can a Bad Ignition Coil Be Distinguished from a Bad Spark Plug?
It is typical to be wary of the spark plugs if you see an odd misfire pattern in your engine since they may also go out spasmodically and lead to faulty combustion in one of the cylinders. But how can you tell the difference between an ignition coil failure and a spark plug failure?
Although the latter is difficult to diagnose, you might be able to check for the problem by probing the spark plugs. Visually inspect the area for any indications of excessive spark plug wear.
Start at the top and scan the electrode for any rust or dirt buildup. Additionally, evaluate if the electrode gap has changed much or not. With a longer distance, the plugs will require more energy to leap the gap, therefore that may be a warning indication.
You would need to do a multimeter test if you wanted to verify the problem by looking at the ignition coil. How much the coil has worn down and how much voltage it generates may be carefully measured using a multimeter.
However, utilizing a set of jumper wires is one approach to see if the ignition coils have burnt out.
Jumper wires, a few screwdrivers, and a person to crank the engine are all needed for the test.
Place the metal head of the screwdriver on one of the three pins within the ignition coil before removing the spark plugs from the coil. After that, unplug the battery’s positive terminal and set the screwdriver in a clamped position with the jumper cable.
Then, have the engine started. Bring the other screwdriver close to the attached screwdriver’s metal end while the engine is running, and you should see sparks fly out.
The coils can be good, or it might be a low voltage current. You would need to do a multimeter test to find out.
What Creates Ignition Coil Failure?
The majority of ignition coils are strong parts, however, neither they are unbreakable nor are they intended to live forever. The most common cause of ignition coil failure is faulty spark plugs or plug wires.
Therefore, your ignition coils may experience early failure if the fuel-to-oxygen ratio in your car is either rich or low. The heat and vibration from the engine might also harm the ignition coils. However, most cars may travel 80,000 to 100,000 miles before needing a new ignition coil.
Is It Safe to Keep Driving With a Faulty Ignition Coil?
Other components of the car, such as the catalytic converter, the powertrain control module, and even the engine, might be harmed by a malfunctioning ignition coil. To prevent more serious issues later on, a damaged coil has to be changed straight away.
Different spark plug sizes by Gzuckier / CC BY-SA 3.0. In most cases, spark plugs are to fault for ignition coil issues, although they can also display fine readings despite physical damage and weakened insulation.
How Can You Keep Your Ignition Coils Last Longer?
To keep your coil functioning correctly and efficiently, take these safety precautions:
- Regular spark plug inspections are important because, as we previously indicated, malfunctioning spark plugs can overstress the coil and cause early deterioration. To avoid this, keep the plugs in good working condition.
- Make sure there are no oil leaks in the coil casing and pay close attention to the wires that link the coil to the electrical system. These are frequently good indicators of issues because, if there has been a recent drain issue, they will look toasted.
- To make sure that your automobile is in excellent operating condition, have frequent service inspections, pay attention to the manufacturer’s recommendations, and undergo routine maintenance.
What Is the Lifespan of Ignition Coils?
Ignition coils should have a lifespan of about 100,000 miles. However, many things can make that mileage less. Coils for ignition function in harmony with spark plugs and other components of the engine. When one component fails, the other is forced to work harder. As a result, the general health of the engine affects the ignition coils’ longevity.
The Conclusion
The signs of a damaged ignition coil might be mistaken for those of worn spark plugs. And despite any visual issues you may see with the spark plugs, you should still have a qualified repair check on your car for damaged ignition coils.
The spark plugs themselves and a circuit failure are two of the primary causes of ignition coil damage. The best approach to identify this problem is with a resistance meter.
But not everyone is adept at using this gear. Therefore, as a general rule, have your car’s ignition coils checked at every periodic repair and replace the set of spark plugs as needed.
Ignition coils are crucial electromagnetic components that increase a car battery’s 12V to almost 100000V. The engine’s cylinders can be ignited and spark-ignited with 100000V, which is sufficient to enable fuel combustion and allow the automobile to run. Any abnormalities with the ignition coils have the potential to seriously affect how the car operates.
Because of this, automobile owners should keep an eye out for any ignition coil problems. These signs include backfires, rough starts, poor mileage management, and misfires in the engine.
Fortunately, as previously described, replacing ignition coils is a straightforward process. Don’t wait for your car’s issues to get worse. As soon as you notice the above symptoms, fix them.


Nyangano Maurice specializes in vehicle troubleshooting and has more than 10 years of experience in the automobile industry. Over many years of experience as a car mechanic, he has acquired a broad range of skills, including engine repair, brake systems, electrical systems, and more. He frequently hosts community workshops and training programs to help motor vehicle owners understand their vehicles better.