Every car has an engine at its core that is propelled by a series of carefully planned, timed explosions. A concentrated mixture of fuel and air is ignited by a strong spark at the start of this combustion. From this point, energy is produced to drive your car off into the distance.
Even so, the engine will eventually reach an age where its source of combustion may stop working. Because your ignition coil needs to be replaced soon, we’re looking at how much it will cost to do so.
But how might the ignition coil malfunction for such a crucial component? And it experiences a lot of strain, as does everything on a car eventually. Imagine the many high-voltage zaps that occur as the battery discharges and the spark plugs receive them.
The ignition coil could only take so much abuse as the one who caused this to occur. You might be surprised to learn that the cost of replacing the ignition coil for this important piece of equipment is not as high as it first appears to be.
What Information About the Ignition Coil Do You Need to Know?
It would be helpful to understand the ignition coil’s purpose before talking about the fabled replacement cost. What part does it play in an engine’s combustion process, more importantly? As was already established, the ignition coil is ideally situated between the battery and the car’s spark plugs.
You may already be aware that the compressed mixture of fuel and air inside the engine’s cylinders is ignited by a spark produced by the spark plugs.
This explosive force causes it to ignite, pushing the pistons up and down and generating rotational power. On the other hand, the battery provides the necessary voltage so that the spark can ignite in the first place.
The spark plug and battery cannot, however, be connected directly. Because of this, the 12-volt battery is unable to provide enough voltage for the spark plugs to operate effectively. In other words, there is not enough voltage to produce a significant spark.
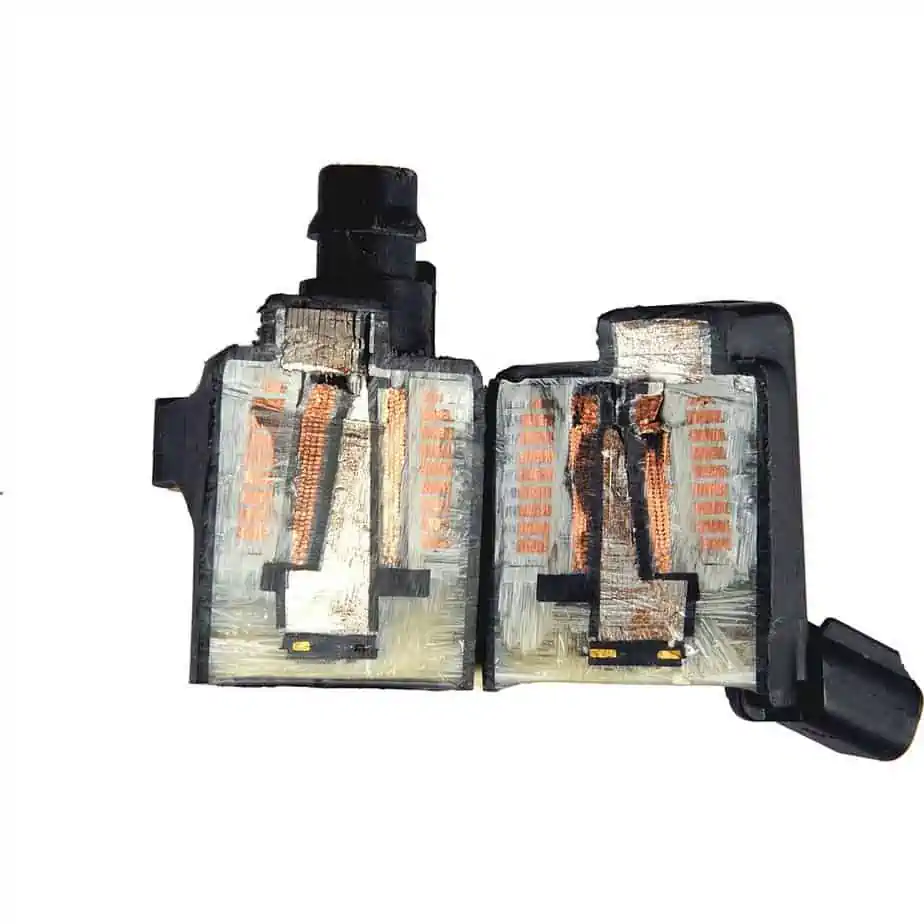
The ignition coil is what we have in light of this. The ignition coil serves as a transformer, and this has been a consistent feature of its construction for the past 100 years or so.
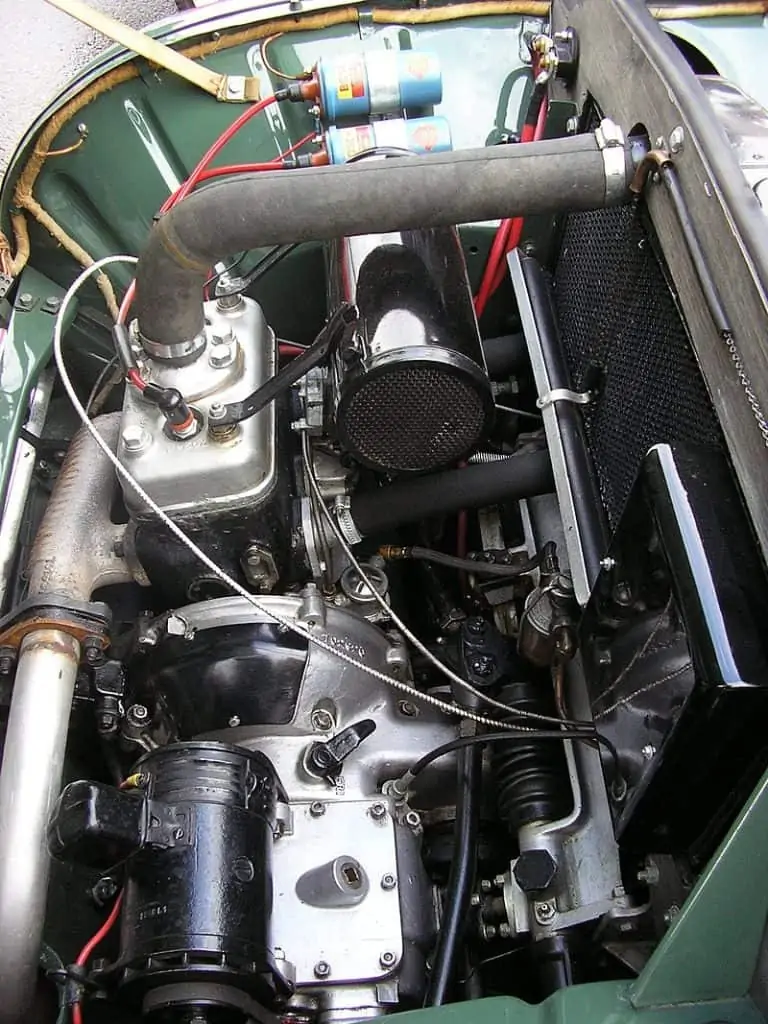
A car ignition coil by Aceonhost / CC BY-SA 4.0. It’s challenging to start a car with a defective ignition coil. The ignition system may malfunctioning if you turn the key in your car and get no response from the engine compartment, not even a click.
It increases the battery in your car’s stable 12-volt output and ramps it up to 15,000, 20,000, or even 30,000 volts. The precise voltage needed will vary depending on your car’s powertrain configuration.
Only with such a high voltage would the electrical current be sufficient to ignite a huge spark. It accomplishes this via the so-called magic of electromagnetism.
How Does the Ignition System Work?
A magnetic field is produced around a conductor, such as a coil of wire, when electrical current passes through it. It may effectively store and increase the overall electrical output and is sometimes referred to as a “magnetic flux.”
In addition, a phenomenon known as a “collapsing magnetic field” is applied by the ignition coil. Two sets of winding coils are often included in the ignition coil.
The battery’s positive and negative terminals are then joined by both. The coil of wire indicated earlier may have 150 to 300 turns in the primary winding.
The secondary winding, on the other hand, often contains 100 times that many turns, or between 15,000 and 30,000. In reality, the magnetic field is created when the battery feeds the primary winding with all 12 volts.
The ignition system of the car will then turn off the current flow to the primary winding when a spark is required at the spark plug. This will result in a sudden collapse of the magnetic field. By the time the primary winding is finished, it will have generated a voltage of about 200 volts, which will then cross over.
As a result, the secondary winding now produces 20,000 volts of voltage, which is about 100 times more than before.
The secondary winding’s ability to produce a voltage that is substantially higher than necessary for the spark plugs to ignite is made possible by mutual inductance.
The primary and secondary windings are often wrapped around an iron core inside the ignition coil. The magnetic field becomes stronger and more concentrated as a result, which increases the effectiveness of the ignition coil.
What are the Many Kinds of Ignition Coils That You Need to Be Aware of?
An ignition coil for a car is designed to last for a very long time, often at least 100,000 kilometers. It frequently becomes worn over time as a result of deteriorating insulation.
It could also fail too soon from prolonged exposure to heat, moisture, shoddy wiring, or a voltage overload. Overall though, you shouldn’t have to worry about ignition coil replacement costs all that often.
However, when the time comes for you to consider that, do pay attention to the type of ignition coil your car is equipped with. There are four primary types of ignition coils to start with:
1. The Conventional Ignition Coil
These utilize a conventional breaker point-type ignition and are outdated. Through a resistor, the primary winding is powered by the battery. Before reaching the spark plugs, it flows to the distributor cap.
However, the ignition coils on these mechanical distributors are ineffective. Additionally, they need to be replaced every 12,000 miles or so due to their lower durability.
2. The Electronic Ignition Coil
The traditional system is most like it. But it makes use of a pickup coil as opposed to a distributor cam and breaker points. To activate the electrics, the control module receives this signal.
However, even though it was more dependable, the distributor shaft’s input was still necessary. After about 120,000 miles, the latter can start to experience gear wear, which could interfere with appropriate spark timing.
Dual ignition coils (blue cylinders, top of picture) by Liftarn / CC BY-SA 3.0. These cars, which only have one ignition coil, won’t even turn on if the ignition coil malfunctions. The engine might at least start on a more recent vehicle with several ignition coils. However, the start-up procedure won’t be easy or painless. Keep in mind that the ignition coil is not the cause of the problem if you hear a “click,”
3. The Distributor-Less Ignition Coil
The distributor-less ignition coil system, an improved version of earlier designs, enables more energy to be combined from many coils.
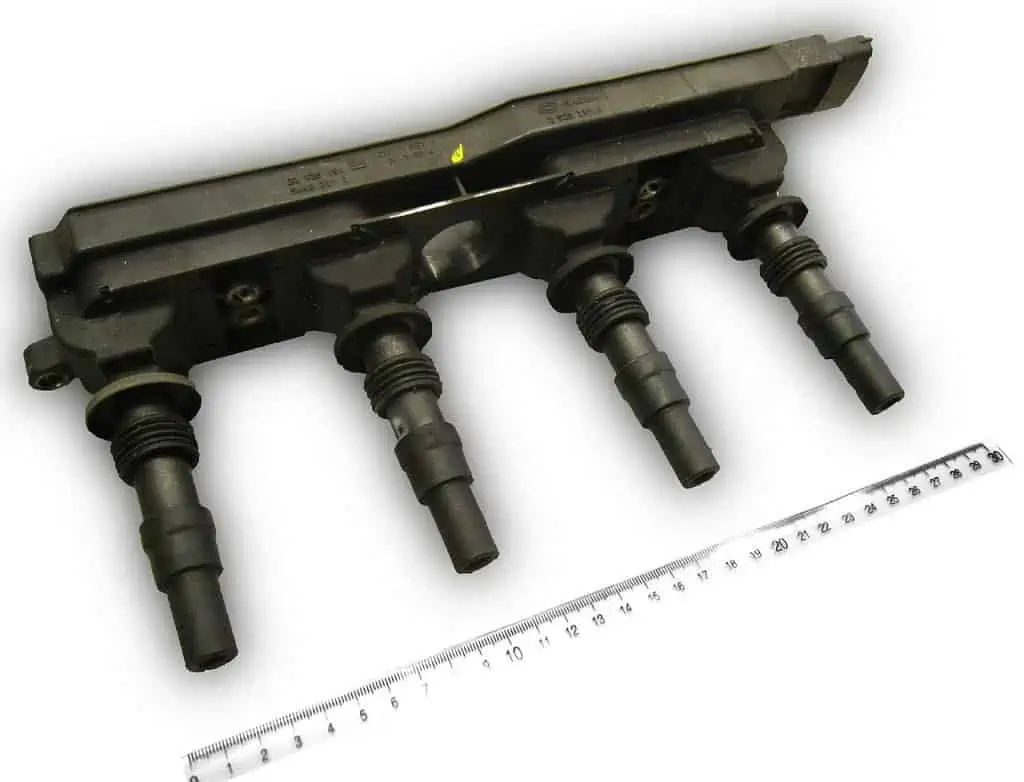
A magnetic triggering system is used to identify the engine speed and crankshaft position in this “coil pack” of ignition coils. It can then be evaluated to determine the ideal spark timing for the most effective combustion.
4. The Coil-On-Plug Ignition Coil
The coil-on-plug design, the most recent development in ignition coils, incorporates all the electrical controls of a distributor-less ignition. However, each coil-on-plug only serves one cylinder, as opposed to two cylinders that would otherwise share a single coil.
Since they may frequently be attached directly to the spark plug, you no longer require spark plug wires as well. It is significantly more potent, with outputs of up to 50,000 volts.
What Signs of a Failing Ignition Coil Should You Watch Out for?
How would you know if your ignition coil was about to fail? There are a few indicators you could watch out for to determine whether you need to consider the expense of an ignition coil replacement.
Just be aware that not all of these warning indicators point to a malfunctioning ignition coil. Some may be brought on by a battery with insufficient or excessive voltage.
However, we can at least exclude the possibility that the ignition coil is the cause. Depending on how bad your ignition coils are—whether they are barely functional or entirely worn out—the symptoms will change. Here are a few of the most typical indications of a faulty or malfunctioning ignition coil:
1. The Car May Be Challenging to Start
First things first, a damaged ignition coil makes it difficult to start the car. Turning the key in your automobile and hearing nothing from the engine compartment—not even a click—is a strong indication that there is a problem with the ignition system.
This symptom would often be present in older vehicles with only one ignition coil for each cylinder.
If so, if the ignition coil fails, these cars with a single ignition coil won’t start at all. In a more recent vehicle with numerous ignition coils, the engine might at least start. But the start-up process won’t be simple and painless. Remember that if you hear a “click,” the ignition coil is not the source of the issue.
2. A Check Engine Light May Come On
When your automobile detects a problem with the ignition system, the check engine light may begin to blink. This is due to the ignition coil, which is an essential component of the ignition, having a direct impact on the engine’s operations. If the check engine light does flash, you may want to get it tested to determine whether the ignition is the issue.
You might scan your vehicle with an OBD diagnostics tool to look for error codes that could direct you to the cause of the check engine light that is flashing at you. Ignition Coil – Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction is displayed when the fault code “P0351” is set specifically for the ignition coil.
3. Car May Experience Engine Misfires
If your car does manage to start, you might or might not discover that the cylinders are firing incorrectly. If this occurs, a malfunctioning ignition coil may be to blame.
Although it hasn’t failed yet, it isn’t in good operating order. The ignition coil may not be able to smoothly and adequately transmit enough voltage to the spark plugs as a result of its current fault.
The ignition coil pack by Cschirp / CC BY-SA 3.0 de. In this “coil pack” of ignition coils, the engine speed and crankshaft position are detected by a magnetic triggering device. The appropriate spark timing for the best combustion can then be determined by evaluating it.
As a result, if the ignition coil generates too much or too little voltage, your cylinders may misfire. This occurs because improper spark timing prevents the proper completion of the combustion process. A misfire might make your car seem like it’s coughing or is just getting started.
4. The Vehicle May Backfire
The burning of the fuel-air mixture taking place outside of the cylinder is referred to as a “backfire” in the automobile industry.
This is quite important since it may cause your engine and exhaust system irreparable harm. As there is still some unburned fuel in the combustion chamber, backfires could still happen.
Following that, it exits the cylinders and enters the exhaust pipe. The plumes of dark or black smoke coming from the exhaust pipe could tell you. The scent of gasoline may be strong in the smoke, smelling much like a recent fuel stop.
In any event, a defective or failing ignition coil may be to blame for backfiring. If you put off repairs for too long, the damage may cost more money in the end.
5. Your Engine Can Stall
As we mentioned earlier, if the ignition coil fails to ensure consistent combustion, your engine may stall. Because a defective ignition coil will cause an irregular amount of voltage to ignite the spark plugs, this will occur.
The engine will stop in the middle of the road if the ignition is unstable since it can’t sustain the combustion for very long.
As we’ve already mentioned, this typically occurs more frequently in older vehicles with a single ignition oil. In more recent vehicles, multiple ignition coils are bundled together to at least partially keep the vehicle running in the event of an ignition coil failure.
You might be able to restart the automobile with just one ignition coil. The stalling, however, is a sign that the ignition coil won’t last long in its current state.
6. Your Vehicle May Jerk, Idle Roughly, or Perform Poorly
You might anticipate poor performance from the ignition coil if it is close to dying. You’ll experience its adverse effects when driving because it probably can’t give enough electricity to the spark plugs.
The ignition coils may frequently malfunction or restart from one cylinder to the next, causing the car to jolt. This trembling can be inconvenient.
Or, because the ignition coils can hardly support the voltage required to keep the engine ignited, it may idle quite erratically. Not to mention, even if your car was still able to go, it could not have enough power.
The number of active cylinders decreases in contemporary cars when one or more ignition coils fail. When accelerating, there may be noticeable hesitation.
7. The Car May Experience a Significant Drop In Fuel Economy
Numerous factors can be responsible for poor fuel economy. A defective ignition coil would be one of them. Your gasoline tank might be severely damaged by all those symptoms mentioned above, such as misfiring, backfiring, jerking, rough idling, or just very poor performance.
The engine must work harder and consume more fuel than is necessary due to a faulty ignition coil.
We’ll then have to deal with all of those problems and inefficiencies, like bad spark timing. Alternately, the gasoline could be burned off by the ignition coil by sending sporadic bursts of voltage to the spark plugs. As a result, a bad ignition coil can make you need to fill up more frequently.
Different automotive spark plug sizes by Gzuckier / CC BY-SA 3.0. Before starting the ignition coil test, you must turn off the engine and detach the coil from the spark plug. After that, secure the spark tester’s one end to the top of the spark plug. Once that is done, attach the other end to the coil output.
You should inspect the ignition coils if you detect an increase in fuel consumption.
The Ignition Coil Testing
How can you know whether an ignition coil has to be replaced? You can do a quick test to see if your ignition coil is damaged. To examine your ignition coils, you’ll need a digital 10 megaohm impedance ohmmeter. A mechanic can assist you in checking this if you don’t have access to it.
You must first attach the ohmmeter’s leads to the ignition coils’ positive and negative terminals to inspect the ignition coils. Then you should read off the numbers it provides.
The typical value is between 0.04 and 2 ohms. Let’s say the ohmmeter shows no resistance at this point. The coil is short as a result of this. High resistance indicates that the coil is open.
You can examine your ignition coil in another way. Using a spark tester is possible. You must first shut off the engine and separate the coil from the spark plug before you can proceed.
After doing so, attach one end of the spark tester to the spark plug’s top. Connect the other end to the coil output once that is complete.
Now that everything is set up, start the engine to see if the spark tester’s light is flashing. The ignition coil is operating properly if you notice a light.
However, if you don’t notice a light, this can indicate that your ignition coils are damaged. To get your car running properly, you must fix these coils as soon as possible.
How Much Does a Bad Ignition Coil Replacement Cost?
Finally, we can come to the heart of this guide: the price of replacing an ignition coil. Please keep in mind the various ignition coil combinations when we respond to that.
One ignition coil may be used for each spark plug in some vehicles, which is typical of more recent models. These might need to be connected to the spark plug wire or they might sit directly on top of the spark plug.
In contrast, your car, which is probably an older model, might only have one ignition coil pack per cylinder. As a result, the cost will differ based on the kind of ignition coil you want.
We’ll also need to take into account the brand and type of your car. The ignition coils in a higher-end vehicle designed for a labor-intensive job or sporty driving should be able to deliver a constant stream of high voltage.
Compared to a set of ignition coils for a normal economy automobile, these modules would cost more. Additionally, the cost difference between replacing your ignition coils at an authorized dealership and an unlicensed business will need to be taken into account.
The latter, in contrast, guarantees the use of OEM parts but is significantly more expensive in terms of charges and labor costs.
Bad Ignition Coil Replacement Cost Breakdown
Below is a comprehensive breakdown of the ignition coil replacement cost. This is important because it will help you work on the costs beforehand.
1. Ignition Coil Replacement Cost: Parts
The ignition coils themselves may often be purchased for between $70 and $375 per. Depending on the coil type and the make and model of the car you’re installing it in, the price may increase.
If aftermarket ignition coils are compatible with your car, you could get away with using them instead of OEM parts from the manufacturer, which would be more expensive.
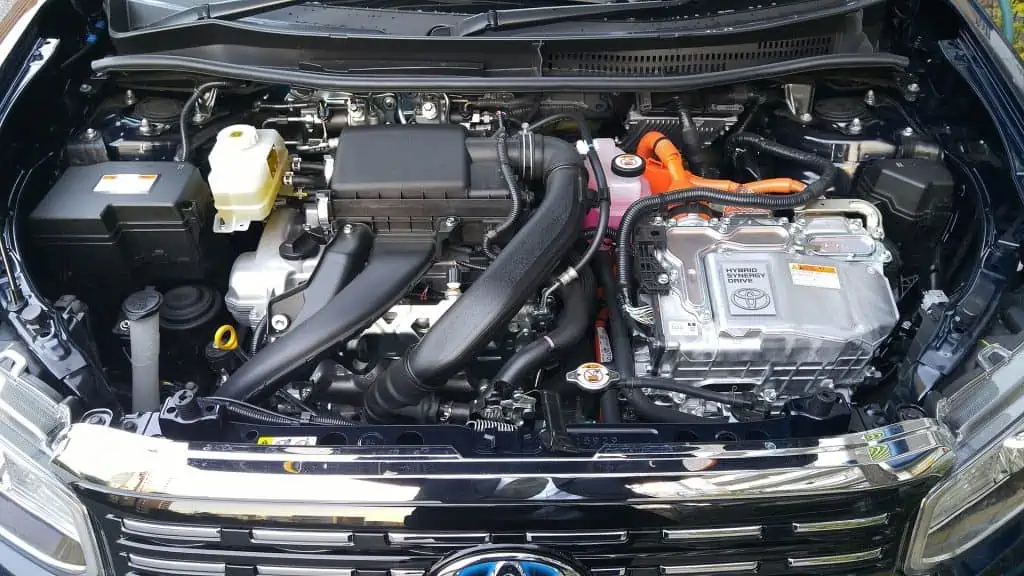
A typical car engine bay by CEFICEFI / CC BY-SA 4.0. Your engine could stall if the ignition coil is unable to maintain reliable combustion. This will happen because a faulty ignition coil will result in an uneven voltage that will fire the spark plugs.
2. Ignition Coil Replacement Cost: Labor
It shouldn’t take more than 0.5 to 1.5 hours to install the ignition coils properly. This is made possible by the ignition coils’ convenient location directly at the top of the engine.
The entire cost of replacing an ignition coil can then be determined by adding up the average hourly labor rates, which range from $50 to $120.
For most autos, we can calculate that the overall cost of replacing an ignition coil rounds up to anywhere between $100 and $550. People can anticipate it to cost between $200 and $300 for the majority of you out there.
Consider performing a few more checks while you’re already in the workshop. Have a specialist check the coil wires, spark plugs, and spark plug wires, for instance.
These can also fail in the future. They may crack when exposed to heat, or they may show signs of corrosion. You might reasonably increase the ultimate ignition coil replacement cost by an additional $50 to $350 if you need to replace them.
While you’re changing the ignition coils, it’s a good idea to take a look at these other parts as well. This will prevent you from needing to schedule a second trip to the shop.
Can You Do This Fix Yourself to Cut Down the Ignition Coil Replacement Cost?
The replacement of an ignition coil is one of the easiest DIY repairs you may perform if you’re eager to avoid paying expensive labor fees. This is one maintenance project you could handle at home if you don’t mind putting some oil on your clothes. Even for beginners, changing the ignition coils is a wonderful introduction to DIY projects.
You will require the following tools:
- A replacement ignition coil
- The Screwdrivers
- A Ratchet and socket set
- The Wrenches
- A service guide for your vehicle
How to Replace Your Ignition Coils: A Step-By-Step Guide
Follow the below steps to help you replace your bad ignition coil.
Step 1
Disconnecting the battery should always be your first step when working on your car. The clamp bolt keeping the cable attached to the terminal can be released using a socket or wrench.
Step 2
Try to locate the ignition coils next. The service manual for your vehicle may come in handy, but you can typically find it at the very top of the engine. They might be fastened to the engine block or elements nearby.
A check engine light or malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) by Wikiuser100000 / CC BY-SA 3.0. The check engine light on your car could start to flicker when the ignition system senses a problem. This is because the ignition coil, a crucial part of the ignition system, directly affects how the engine runs.
Step 3
Next, unplug and eliminate the old ignition coil. They are fastened to the car with screws or bolts. Additionally, you need to unplug the coil’s electrical connectors. Check your service manual to see what should come first and in what order. to unbolt the appliance or to remove the electrical connections.
Step 4
Once you’ve figured it out, remove the ignition coil’s electrical connections and bolts or screws in the proper sequence. However, keep in mind that some vehicles use a single ignition coil to power multiple spark plugs at once. In this case, you will need to note where the electrical connectors go during reassembly.
Reattaching the connectors to the new ignition coil’s corresponding terminals is necessary for it to function.
Step 5
The new unit can be installed there once the old coil has been removed. Remember to reconnect the connectors to the proper terminals on the new coil and complete the process in reverse order. Be careful not to tighten the bolt or screw it too much.
Step 6
Now is the time to start the engine. Check to see if your car idles smoothly and normally while it is in “Park.” If everything looks good, you could take a brief test drive.
How Often are You Likely to Incur the Ignition Coil Replacement Cost?
Once you’ve established that the ignition coils are malfunctioning, you must swap them out. You can replace these on your own at home if you have the right tools. Bring your car to a mechanic, who will be able to replace these coils for you if you don’t have the right tools.
To replace these on your own, you must first unplug the vehicle’s battery. By unscrewing the bolt with a wrench, you can remove the negative terminal. After doing that, you must find the ignition coils. These are typically found on the engine’s top. The engine block will receive them.
Remove the old ignition coil and the electrical connectors using the socket wrench. Install the new ignition coils once everything has been disconnected.
Make sure to tighten the bolts on everything and reconnect the electrical connections. Reassembling everything in its original configuration is crucial. This will guarantee the proper operation of your car.
Reconnecting the battery’s negative terminal and starting your car are the final steps in this procedure. To make sure you don’t hear any misfires or stalling, you should test-drive your car. You have successfully replaced the ignition coils if everything works as it should.
An engine block with six cylinders by Kether83 / CC BY 2.5. Your cylinders could misfire if the ignition coil produces too much or too little electricity. This happens because poor spark timing inhibits the combustion process from concluding properly. Your automobile may appear to be starting up slowly or coughing due to a misfire.
The Conclusion
All things considered, the ignition coils are essential to your car’s internal combustion engine. Your beloved car might not even start without it. So it’s helpful to know that ignition coils are built to be reliable and durable.
There are many cars available, so they might last for the duration of ownership. However, you might still have to deal with the expense of replacing the ignition coil.
Despite their significance, ignition coil repairs are surprisingly not the most expensive car maintenance tasks. A bill of roughly $100 to $500, or only $70 to $375 for the coil itself, won’t do much financial harm to your finances.
Additionally, replacing them yourself could result in significant labor cost savings. By all accounts, the price of replacing an ignition coil is not that bitter a pill to swallow.

Dual ignition coils (blue cylinders, top of picture) by Liftarn / CC BY-SA 3.0

Jim Wicks is the founder of MotorVehicleHQ. With over two decades of experience in the automotive industry and a degree in Automotive Technology, Jim is a certified car expert who has worked in various roles ranging from a mechanic, car dealership manager, to a racing car driver. He has owned more than 20 cars over the past 15 years. Ask him about any vehicle you see on the road and he can tell you the make, model and year. He loves the aesthetics of all things cars, and keeps his vehicles in pristine condition.
In his free time, Jim enjoys getting his hands dirty under the hood of a classic car or taking long drives along the country roads. His favorite car? A 1967 Shelby GT500, a true classic that, according to Jim, “represents the pure essence of American muscle.”